The master production schedule comes as an enterprise feature in the odoo manufacturing module.
Many manufacturing units practice the method of Make to Stock so as to fulfill customer demands. MTS briefly expanded Make to Stock is a strategy used by manufacturing companies in order to fulfill the future demands of the products.
If we take the case of manufacturing industries, we often see that companies produce products in bulk and later sell them. But in the case of MTS, the company analyses the future demand of the product and correspondingly makes the products.
In other words, we can say that in MTS strategy the organization produces products without the manufacturing order rather than just forecasting future demands. In the case of an example raincoat, during monsoon season raincoat is in high demand. Thus its production has to be increased during that season.
With Odoo 13 comes the cool feature of MPS, Master Production Schedule, as a remedy for manufacturing products on forecasted demand. Forecasting demand means based on past demands we analyze the future demand.
Here let us see the working of MPS in Odoo 13 manufacturing.
First and foremost we have to enable the Master production schedule. For that go to Manufacturing -> Configuration -> Settings -> Planning -> Master production schedule.
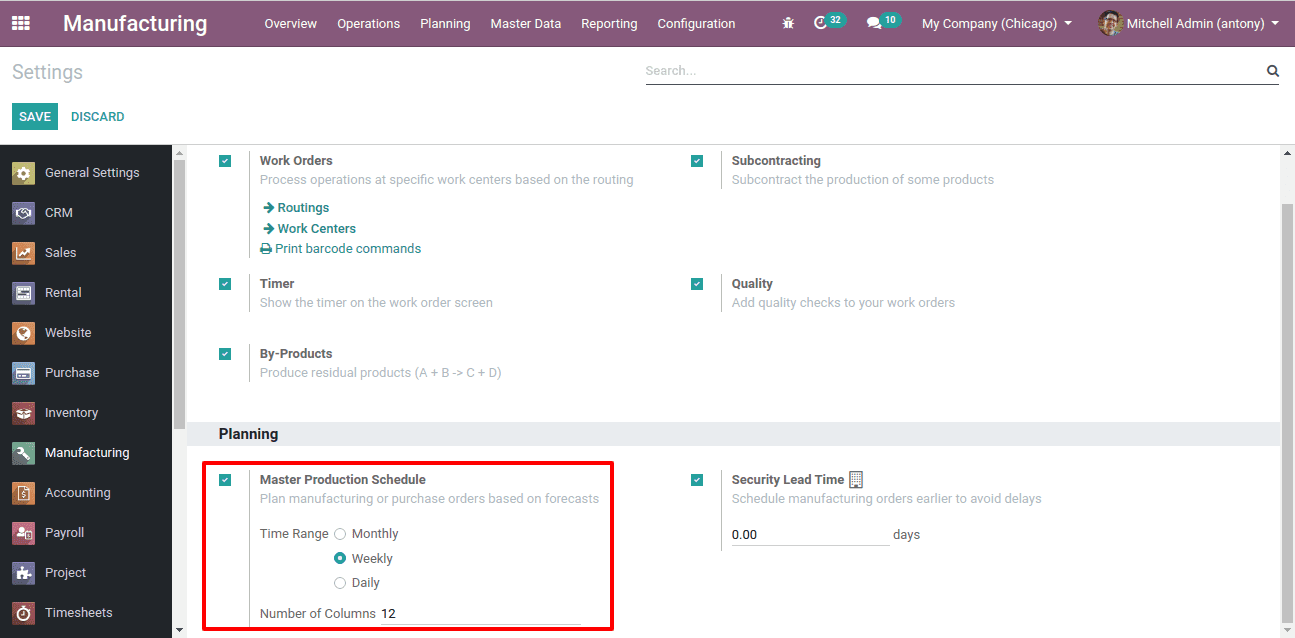
Here we have three-time ranges for a production like Monthly, Weekly, Daily.
Now let’s go to Manufacturing -> Planning -> Master production schedule
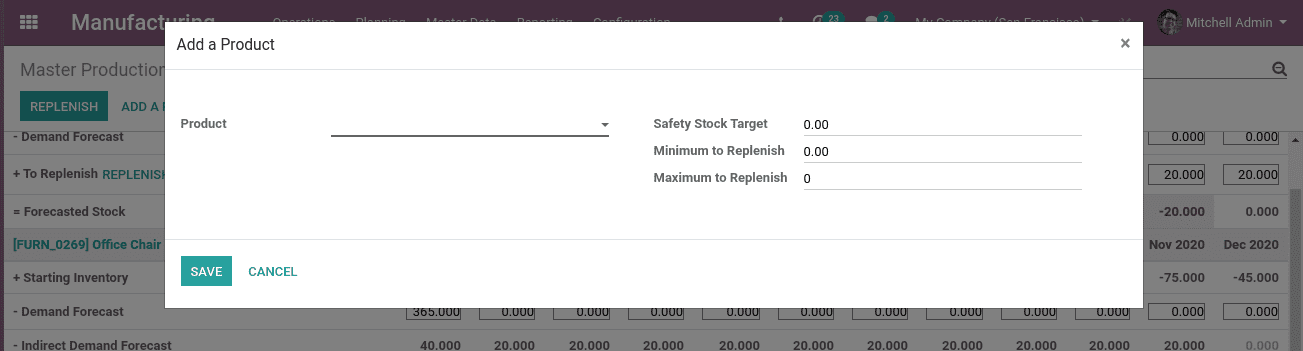
There we can click on “Add a Product”.
Here we wanted to add the product. The route of the product we are adding here must be manufacturing.
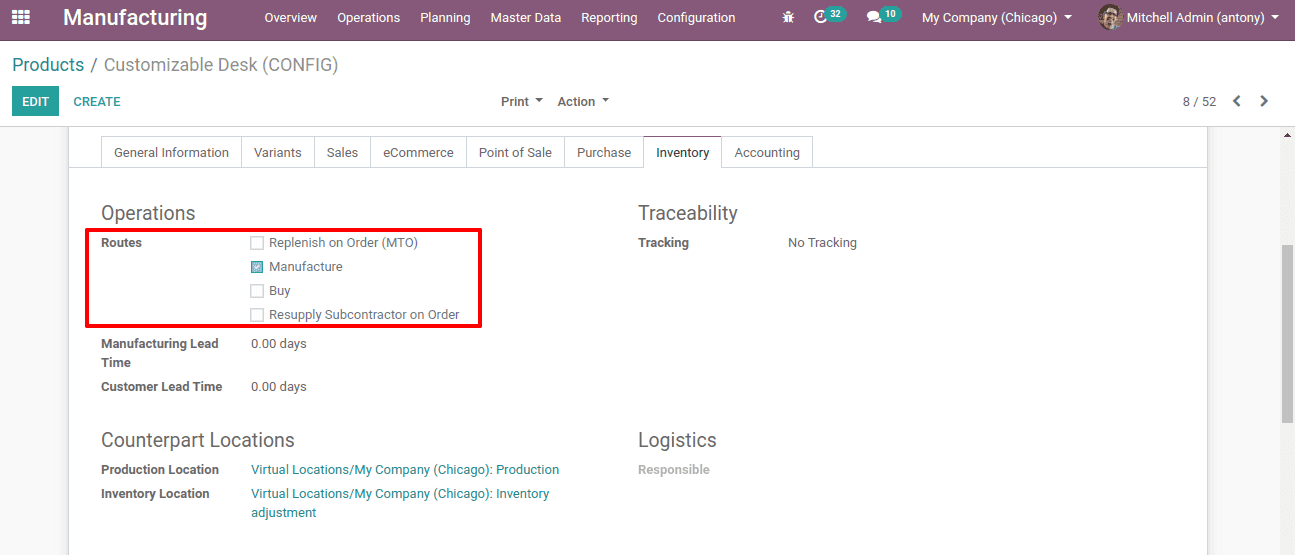
Now let’s add the product to the MPS.
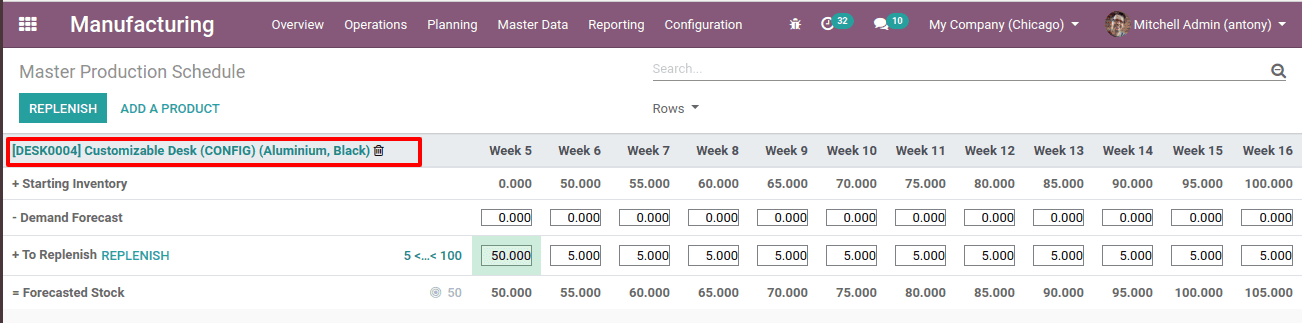
In this picture, we can see some other information also. Let’s check what all are those.
We have given the Time Range “Weekly”. Thus here we have 12 weeks given.

Then we have,
Starting inventory: It is considered as opening stock for the week, much like the forecasted inventory of the previous week.
Demand forecast: It is the forecasted demand for the current week for the product.
Indirect demand: In some cases, we will have indirect demand for a product. It means that the demand for a particular product affects the demand for another product. A simple example of this is, the demand for motorbikes influencing the demand for petrol. Here the demand for petrol is indirect demand.
Note: Both the demand forecast and indirect demand will be deducted from the starting inventory.
To Replenish: Here we can update the product quantity by clicking the “Replenish” button there.
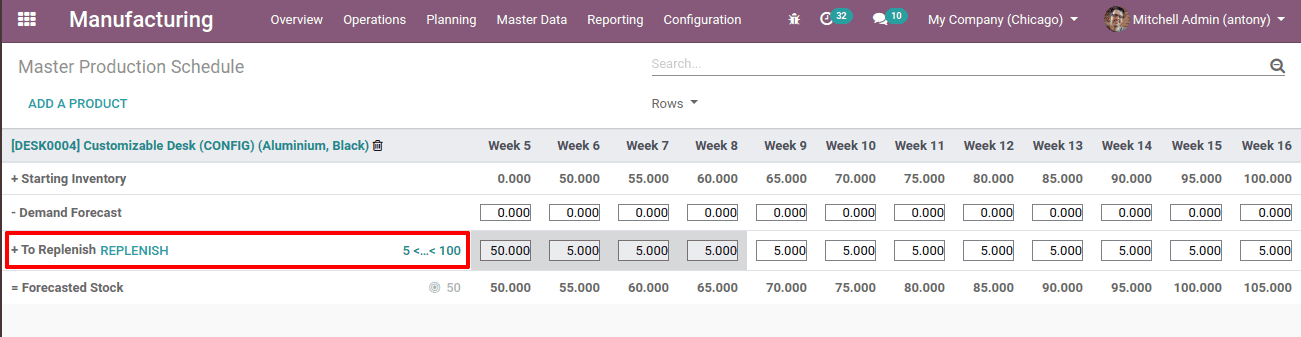
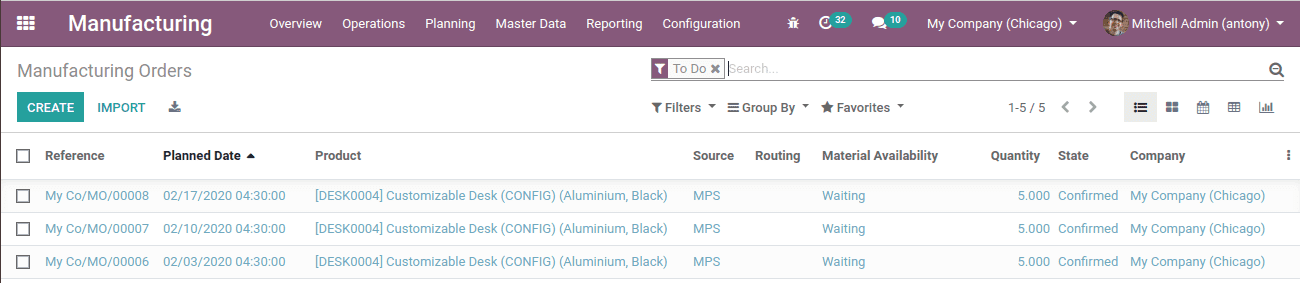
When we click the “Replenish” button, automatically the manufacturing order will be generated.
We have to mention the minimum and maximum quantity before entering the product into MPS.
Here we have,
Safety stock target: This is the stock of products we keep as a safety in terms of contingency. For that, we keep a targeted stock.
Minimum to Replenish: It means when the product reaches the minimum quantity, we set a manufacturing order by clicking the “Replenish” button.
Maximum to Replenish: It is the product quantity we can replenish to the maximum.
Forecasted stock: It is the stock we target to have in the inventory at the end of the week or month as we set.
Therefore, Forecasted stock = Starting inventory – Demand forecast – Indirect demand + To Replenish
Let’s check with an example.
Here we have added a customizable desk to MPS.
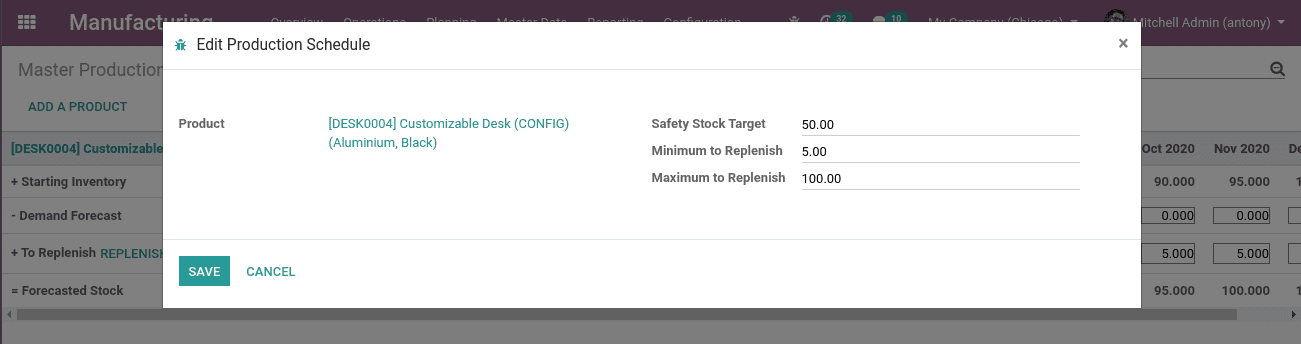
We have set the safety stock 50, minimum to replenish 5 and maximum to replenish 100.
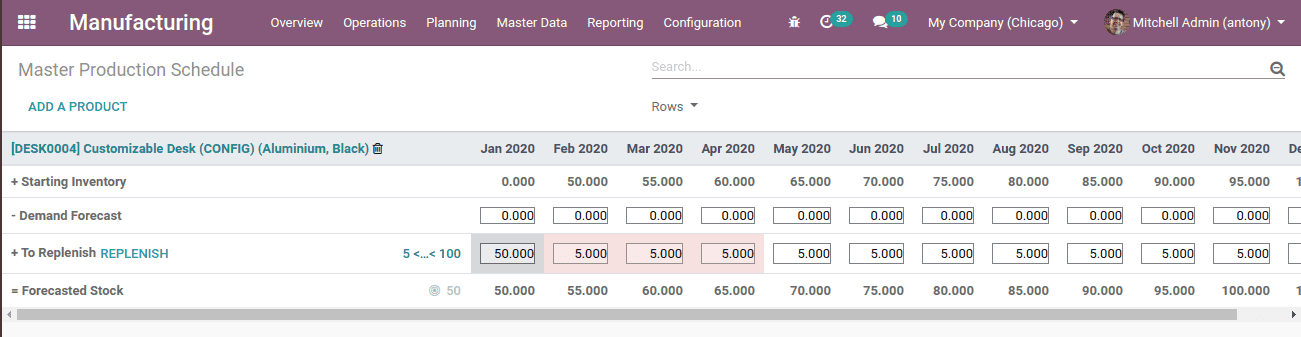
So, the above is the calculation of MPS.
In the first month, Jan 2020 starting inventory is 0, and the forecasted stock is 50. Thus we have to produce or replenish 50 to reach the forecasted stock at the end of that month. Next month the forecasted stock of the previous month is the starting inventory of next month that of Feb 2020. And the forecasted stock of Feb is 55 so to reach that we have to produce or replenish 5 quantities.
We can also add the demand forecast here itself,
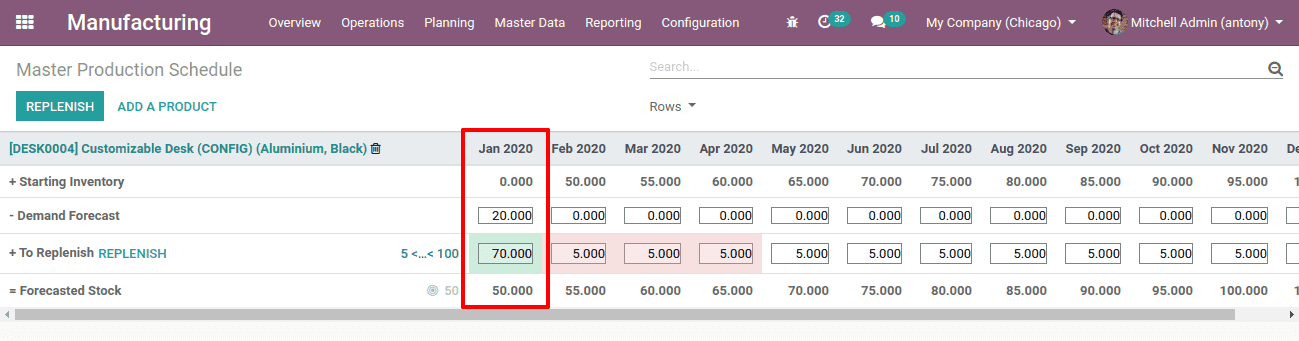
Here we have added demand forecasted 20. Then we have to replenish 70 products to reach the forecasted stock of 50 because 20 products already have the demand and those 20 will be sold.
Now we shall see how the indirect demand for another product is managed.
Indirect demand is the demand for one product influencing the demand for another product.
Here we shall add the tabletop since it is the component product of the above customizable desk.
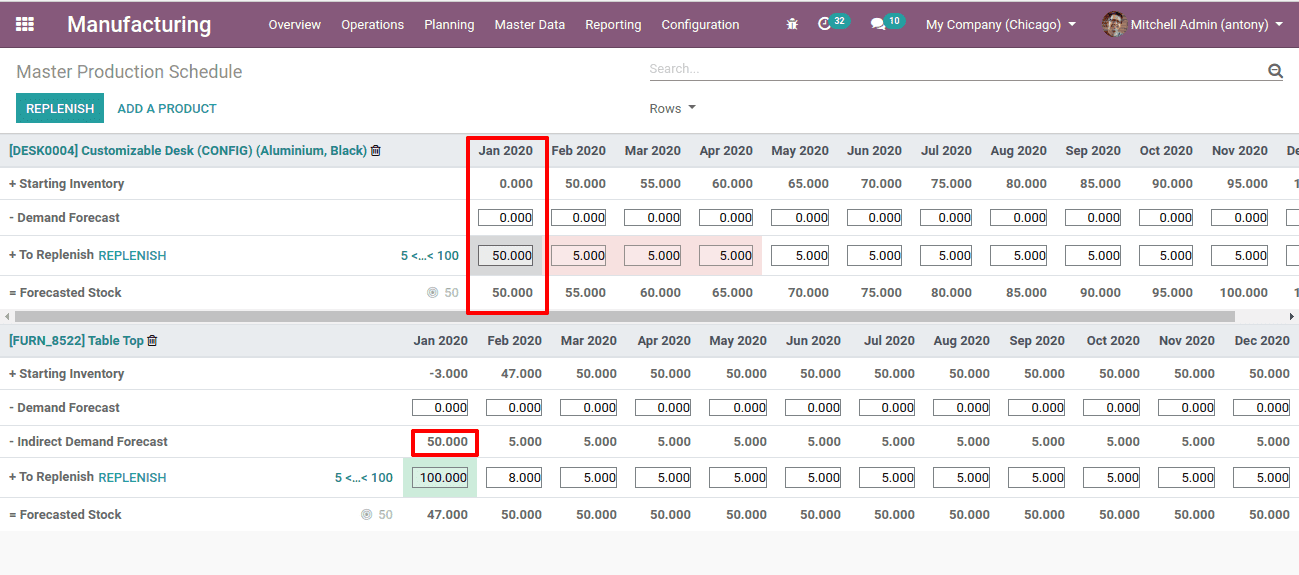
When the demand for Desk increases the indirect demand for the tabletop increases. Hence the demand for the desk is the indirect demand for the tabletop. Here when the demand for desk changes the indirect demand for tabletop also changes correspondingly.
This is how Master Production Schedule is carried in Odoo 13.


