Odoo ERP is indispensable and also crucial in the inventory management of an organization. The functional features and advantages of Odoo make the managing and tracking of stock of business easy and accurate, and thus the efficiency and productivity of the business improve. Using Odoo we can effectively and efficiently manage the internal stock management that occurs in the company.
Inventory management is a crucial element in a business. Unless there is no effective system to manage the inventory there will be many malfunctions happening in the company. The firm will lose its efficiency and productivity and it will lose credibility consequently. If there is no good inventory management system the firm will have to face many challenges like understock and overstock of products, indisciplined use of the warehouse, inefficiency in product tracking, inability in meeting customer demands and so on.
Odoo is so flexible and efficient in managing the inventory of any type of business may it be small or large, simple or complex. Odoo 13 is an all in One ERP solution with many advanced features like product traceability, dropshipping, double-entry inventory, cross-docking, multi-warehouse management, routing, and so on. Also, it gives more efficiency by integrating it with all other modules like accounting, purchase, sales, manufacturing, maintenance, repair and so on.
Here we are explaining about routing in warehouse management.
Routing is all about the order picking process, where the items are selected from different storage locations based on customer demands. In simple words, Route is the pathway a product ought to follow. Routes are created based on the product ordered, location and warehouse. For doing a procurement activity Odoo searches for routes based on the sales order or product.
Odoo aids to have a smooth workflow in the warehouse. Here we have routes that incorporate some rules like procurement rule, push rules, pull rules and so on, which facilitates the easy and smooth movements of the products inside the warehouse and to the customers.
How does it all work?
A warehouse is a physical place or location where the products or goods are stocked. Here in Odoo we can create multiple warehouses and can conduct smooth inter warehouse transfers.
To create multiple warehouses go to, Inventory > Configuration >odoo warehouse management > Warehouse > Create
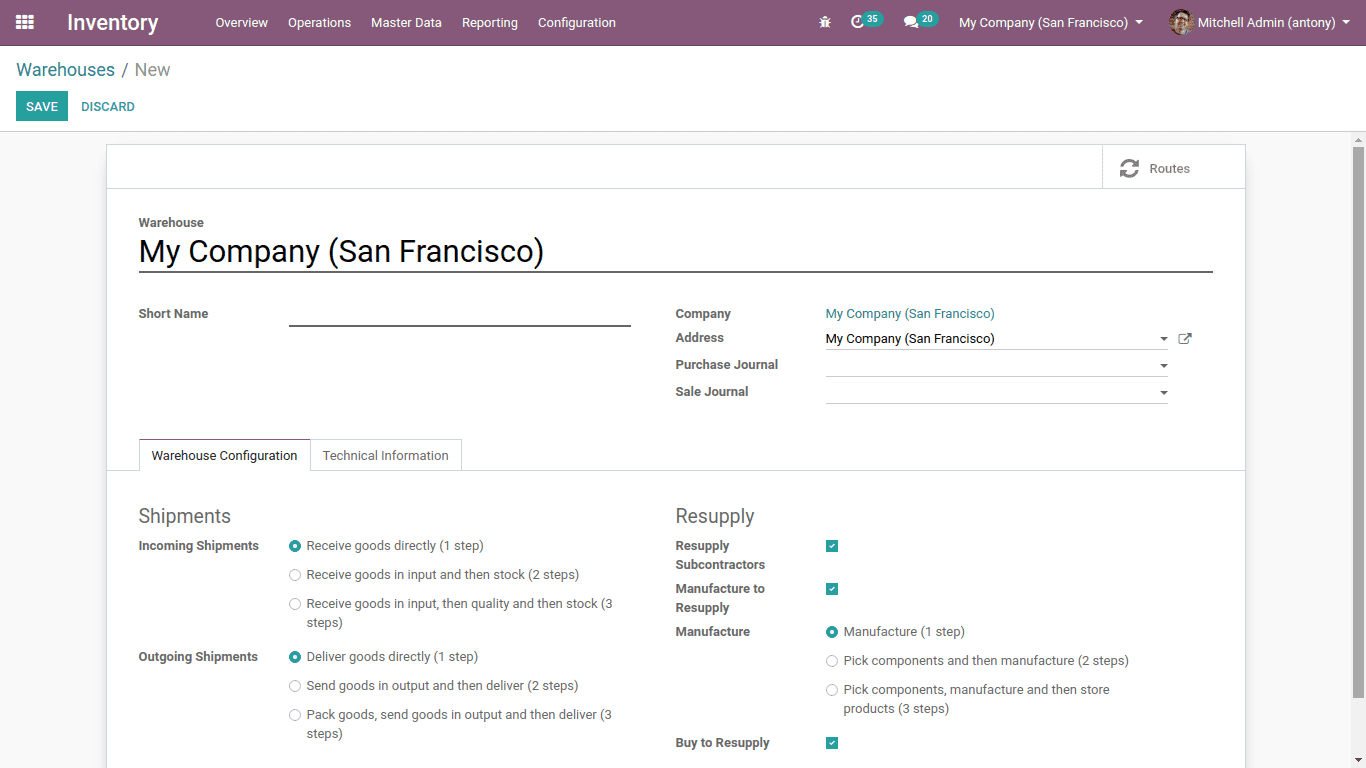
Here we can create a new warehouse.
If there are multiple warehouses in our company we can select any of the warehouses for re-supply. Under shipments, we have incoming and outgoing shipments. There we can select the steps of receiving and delivering products from the warehouse.
Location
Then we have a location in Odoo warehouse. Location is a particular place like a shelf and so on where stock is kept. We can also configure and create multiple locations under one warehouse. All the products pass through locations.
In Odoo we have 3 locations, namely:
Physical location: This is the location in our warehouse where stocks are kept or stored, like shelves.
Partner location: This location is not in our warehouse but its the location of our customer’s warehouse.
Virtual location: This is the location that does not have a physical existence but useful at the time of loss of stock from inventory or the stock which is yet to come to the warehouse. We shall keep all those products under a virtual location.
Configuration of Location
Go to Inventory > Configuration > Warehouse management > Locations > Create
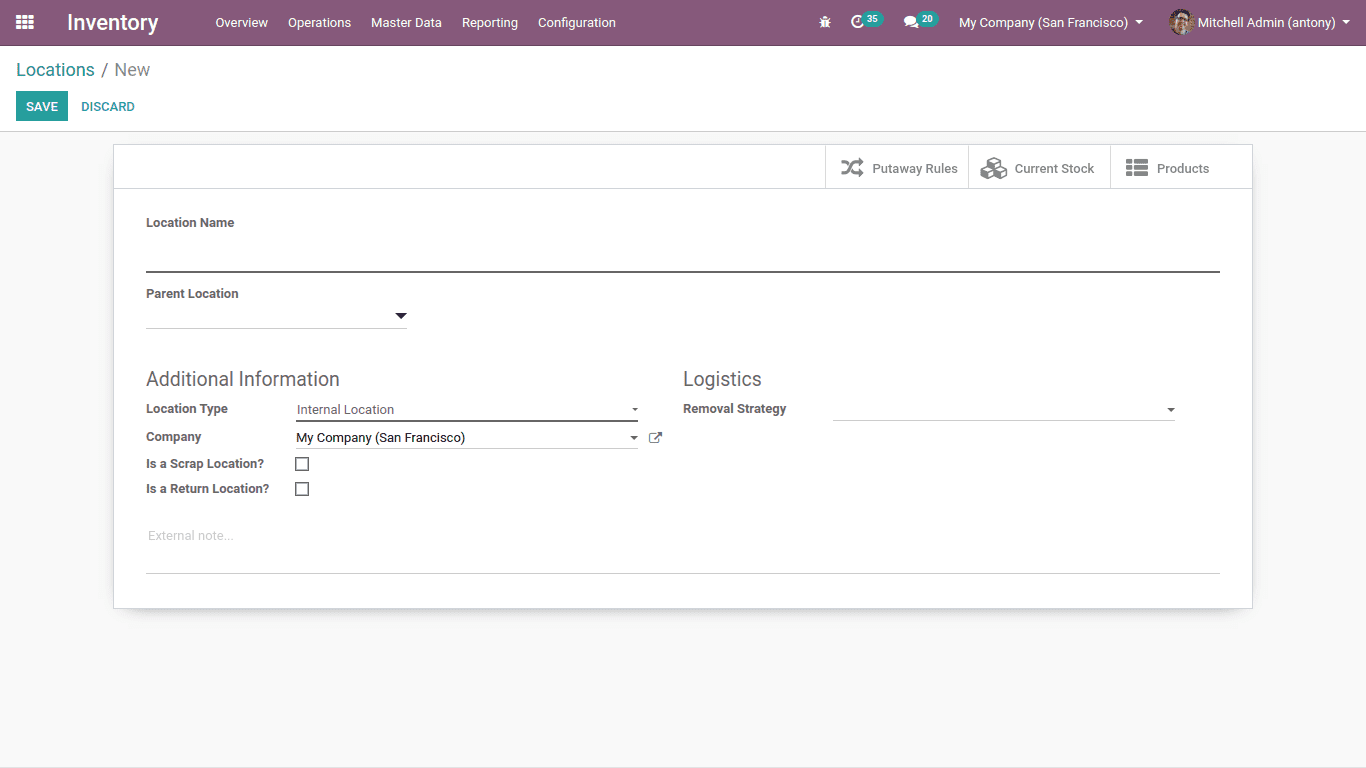
Here we can create a location.
Routes
Routes are the pathway through a product that arrives at the warehouse or goes out of the warehouse. Here we can configure a single step or we can configure multiple steps in the routes. When we create a product we can see an option of ‘Routes’ to be checked. It assures the tracking of the product throughout the warehouse.
We can create new ‘Routes’.
Inventory > configuration > Routes > Create
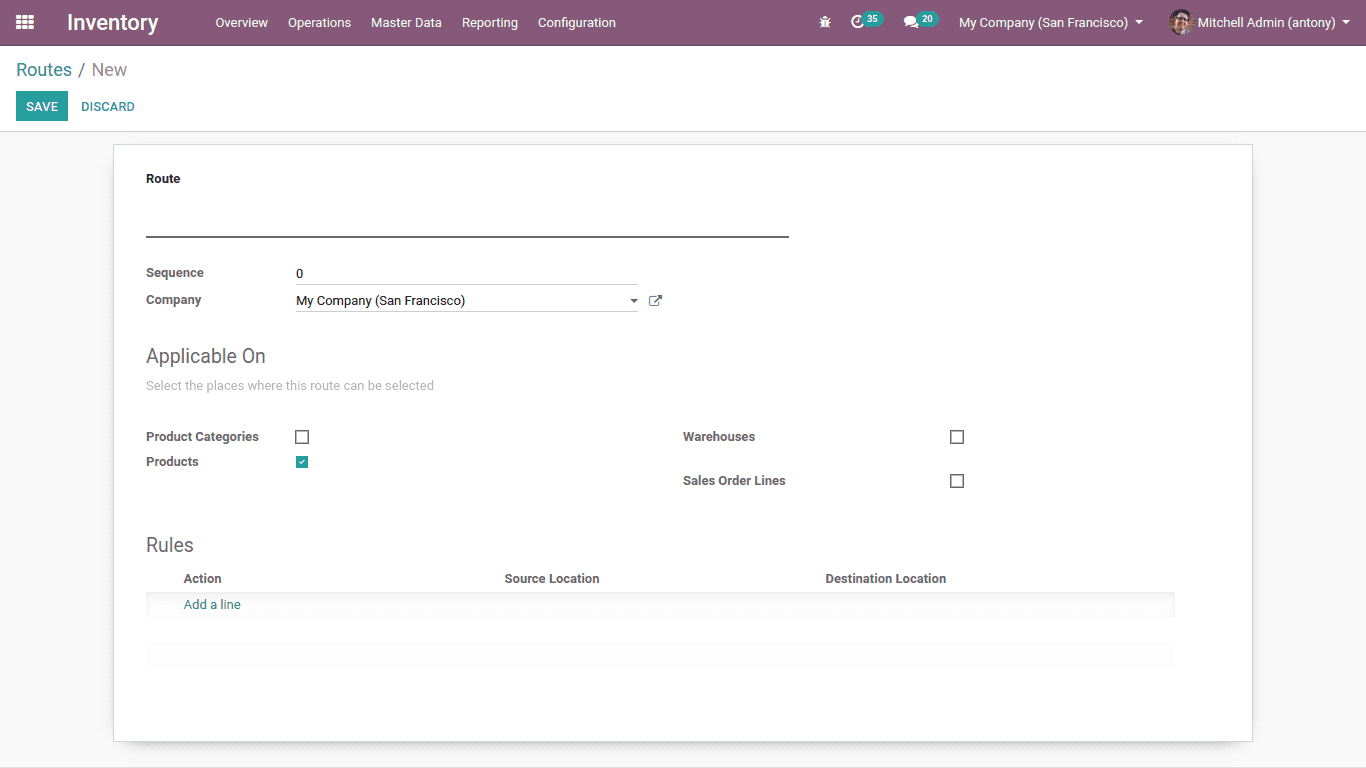
This is the form to create a route.
Procurement Rules
When the customer order comes the company begins procurement inventory. The company only makes those amounts of products as per demanded by the customer. The advantage of this rule is that there won’t be any overstock or understock of products. This decreases the inventory cost.
Three actions are possible under procurement rules.
1. A movement from another location.
2. Triggering of the manufacturing rules generates manufacturing orders.
3. Triggering the buying rule will generate purchase orders.
All these rules help to meet the customer’s order as it arrives. It decreases the wastage of materials, products, time and storage space. Make to Order thus, helps to have the cost-efficient inventory of products.
Push rule
A push rule flow shows how the other points of location are linked to each other. Once a defined amount of products is pushed at the source location a chained step is automatically planned as per the flow specification parameters (destination, duration, movement type, journal). It can be automatically or manually activated.
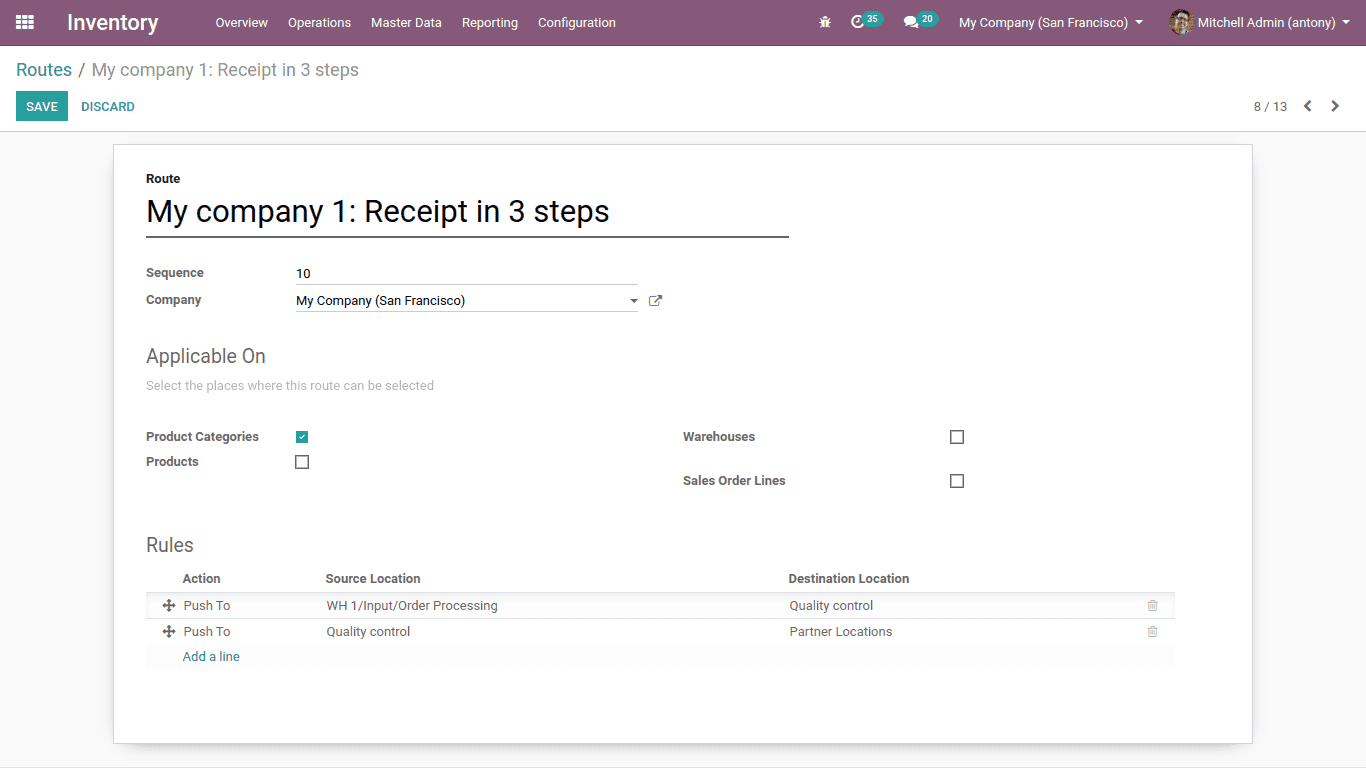
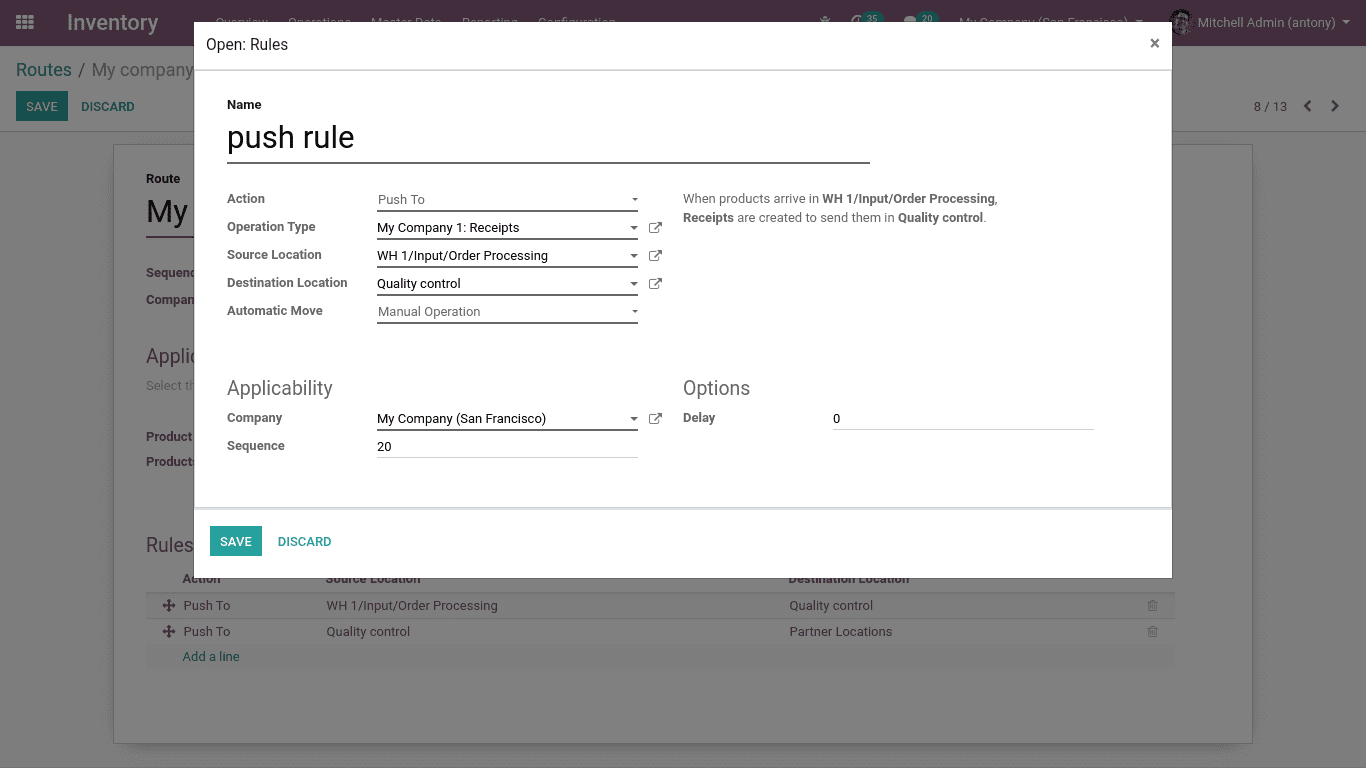
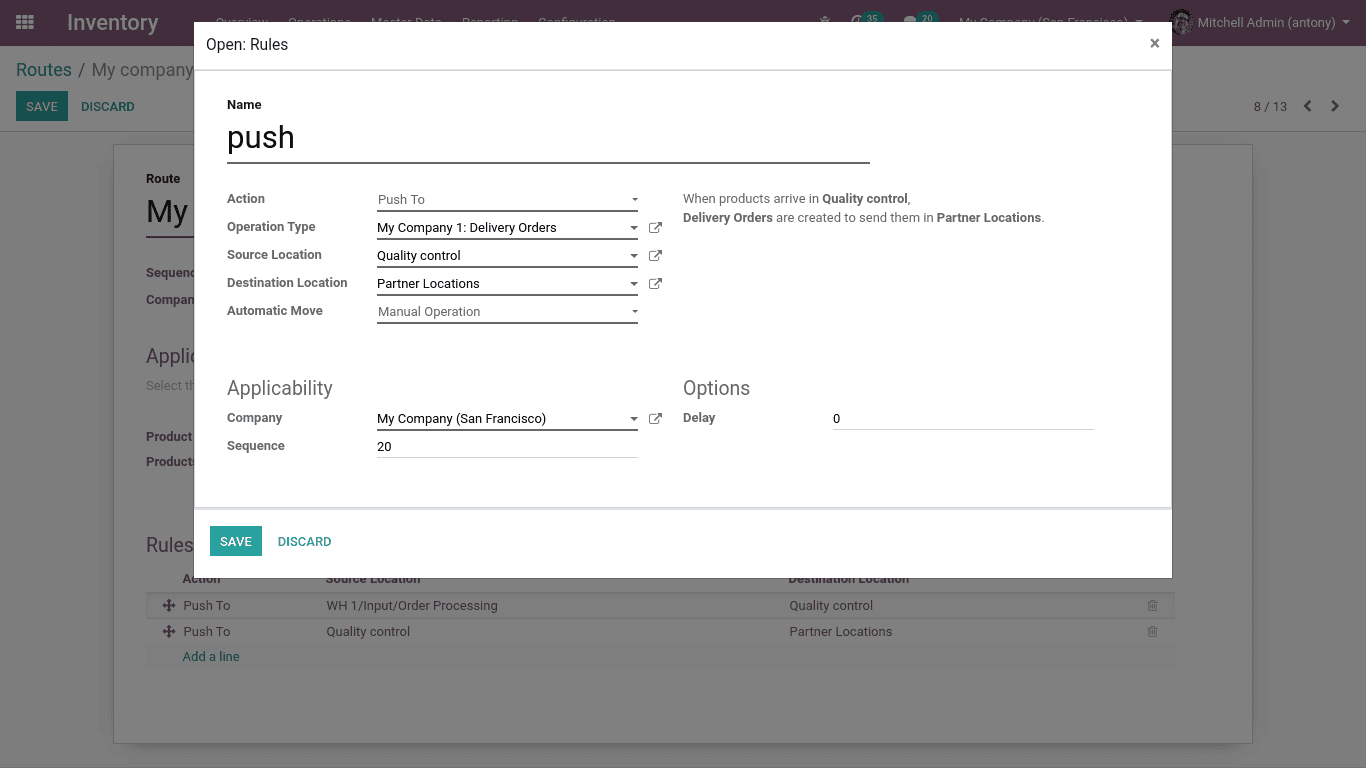
Here when the partner or customer purchases the products the company can easily analyse the quality of it by the help of push rule.
Reordering rules
Reordering rule is the rule that helps is updating the inventory automatically. Here we can set a minimum and maximum quantity and can set ‘Run Scheduler’. When the product reaches the minimum quantity it checks the reordering rules and trigger run scheduler and thus the quantity is maintained. Here we are always able to keep the minimum quantity of product always.
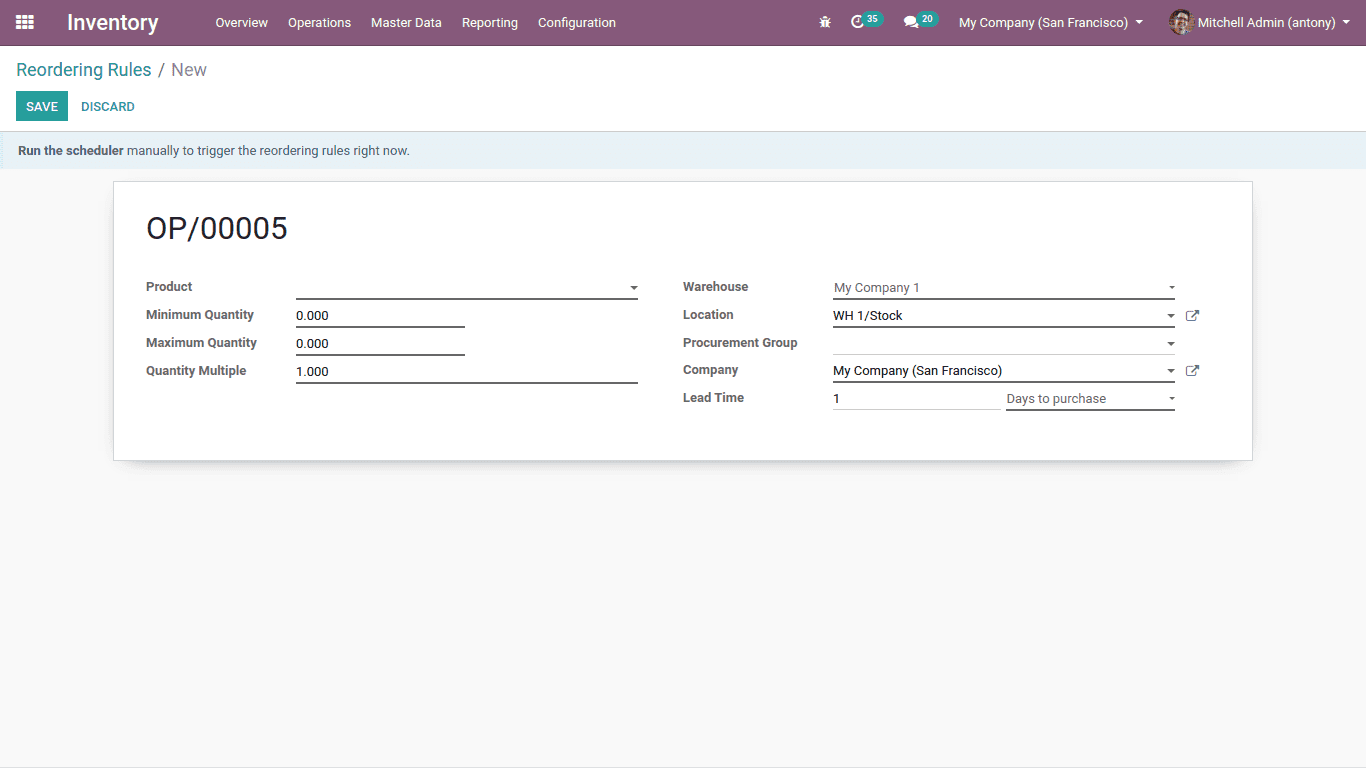
This is the form to create ‘Reordering Rule’
Minimum quantity: It is the minimum quantity of products that must be kept in the inventory.
Maximum quantity: It is the maximum limit of the product should be kept in the inventory.
Quantity multiple: At a time how many products can be ordered.
Procurement group: Here we can set the procurement and picking of the product.

Now let’s discuss some other shipment rules.
Cross-docking: It is a method in the logistics, here we unload materials from an inbound semi-trailer truck or railway car and load those materials directly into outbound trucks, trailers or railcars, with no storage between them.
Dropshipping: Drop-Shipping which moves products directly from the distributor/manufacturer to the customer (could be the retailer or consumer) without going through the usual channels of distribution. The items are sent to the customer directly from the vendor, without going through one’s own warehouse.
Removal strategies
A company uses removal strategies to deliver the best products to its customers.
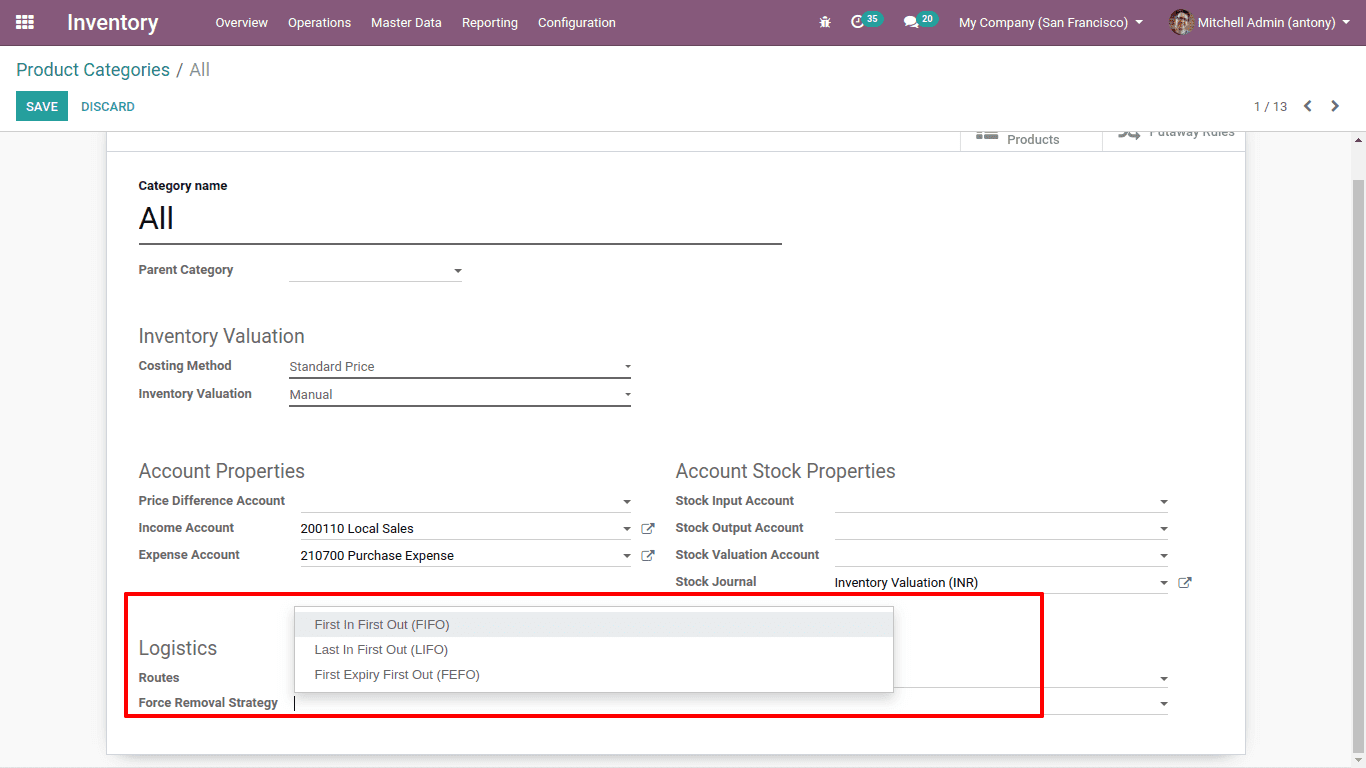
First In First Out: Here the products first arrived in the stock moved out first. Companies dealing with perishable goods use this method.
Last In First Out: Here the products that arrived last to the stock will be moved out first. This method is used by those companies that deal with products with no shelf life, like liquor.
First Expiry First Out: Here the products are removed out of the warehouse as per the expiry date. And for that, we have to set a removal date while creating a lot and serial number for the product.
Expiration dates
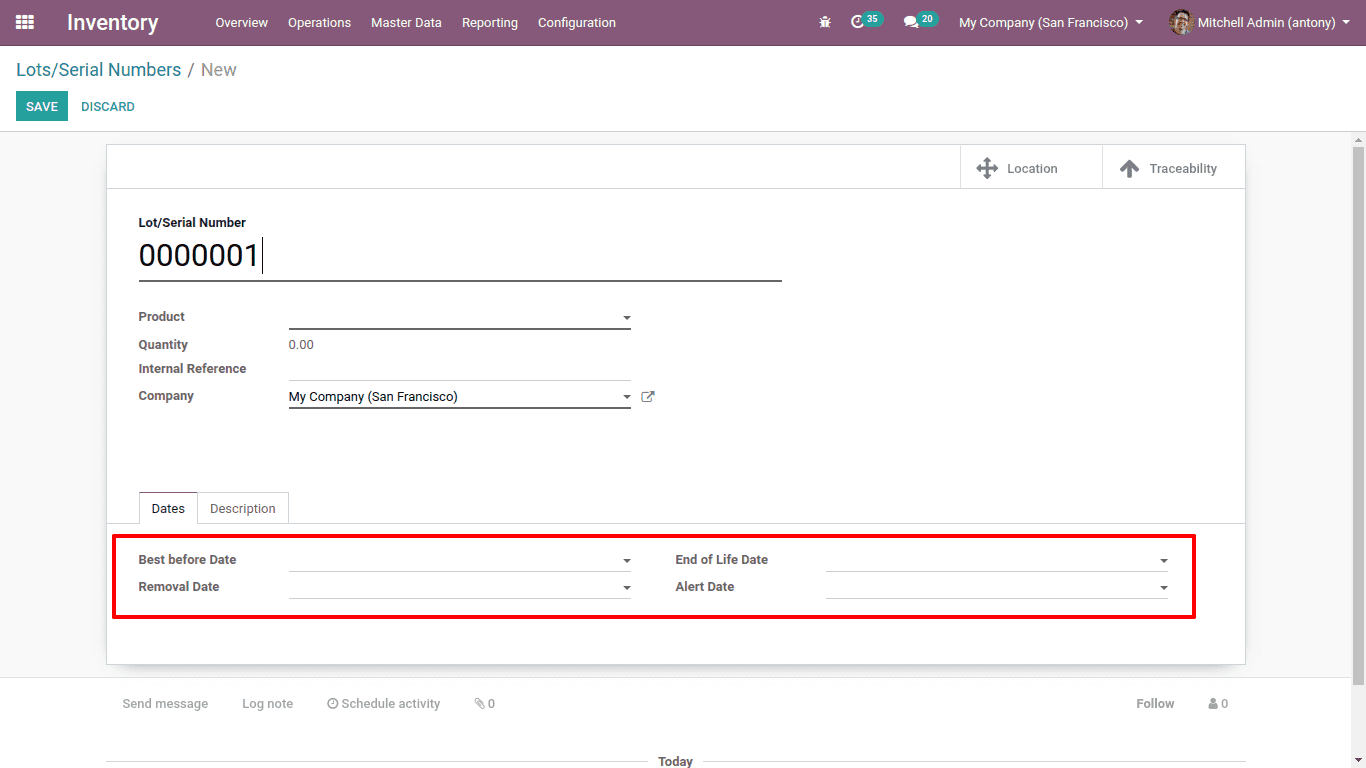
While creating Lots/Serial numbers we have to mention the following dates. It will be helpful in the FEFO removal strategy.
Best before date: This method determines the date on which products start to degrade. This serves as a call for action before the item becomes unsafe for use.
End of life date: This method helps to set the date on which the products is unsafe and not appropriate for use.
Removal date: Helps determine the date the products with specific lot / serial numbers should be withdrawn from stock.
Alert date: Here an alert will be shown regarding the product with specific lot / serial number on the set date
So this is all about ‘Odoo 13 warehouse management and routing’.


