Product costing operations is one of the most difficult duties for a business. Using product costing methodologies, it is simple to assign a definite price to a manufactured product. Inventory valuation can be used by a corporation to determine the value of products in a warehouse. Users can use an Odoo ERP to deal with product price descriptions and immediately value their goods using the costing method feature of the Odoo 16 Inventory module.
Odoo 16 has classified Costing method into three types and they are Standard Price, First In First Out (FIFO), and Average cost (AVCO).
Now let’s check the working of different costing methods in Odoo 16.
Standard Price Costing
The standard pricing is simple to understand. Standard pricing is unaffected by the purchase order price. That is, it only uses the cost field (purchase receipts and delivery have no effect on cost).
In the case of standard price product costing, the cost price is frequently updated manually. In most cases, the product’s price changes once a year or after a certain term.
Let us create a new product and set the costing method as the Standard price, as shown below.
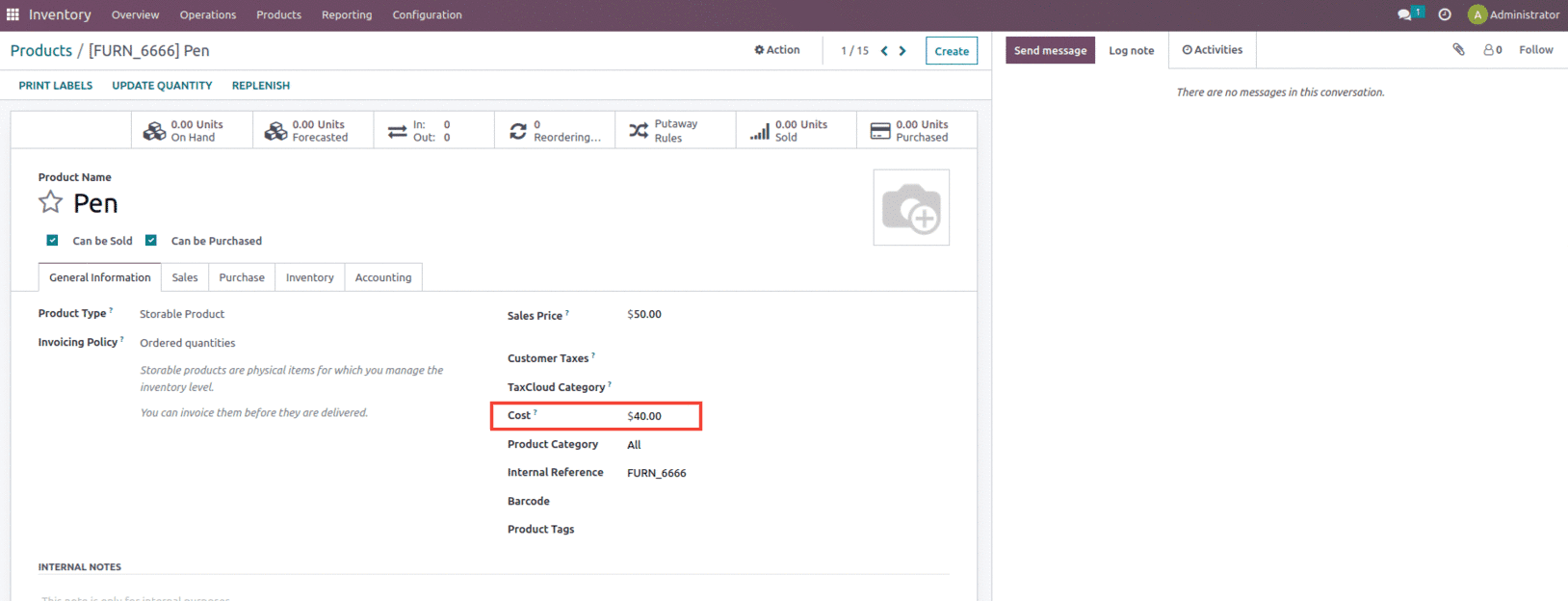
Here you see that the cost of the product is set as $40, and the cost method is set as the standard price.
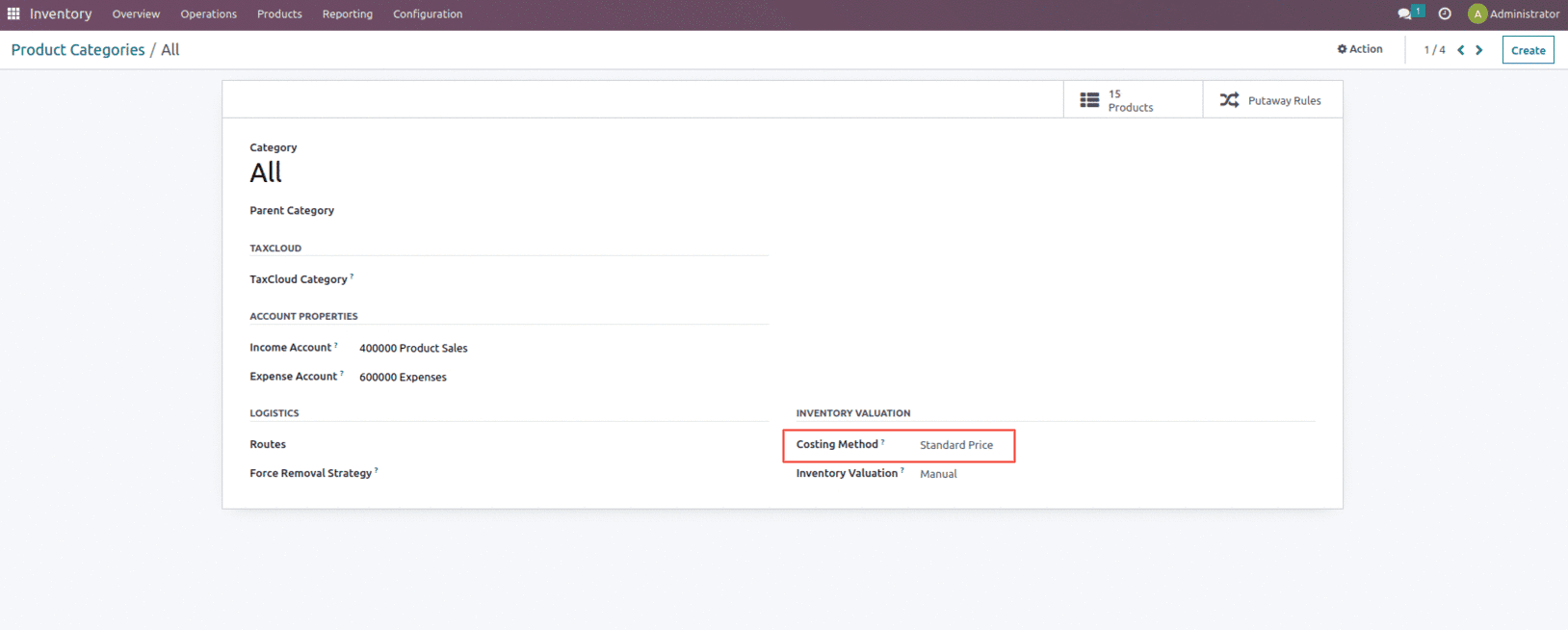
Let’s save it and create a purchase order for the product to check the standard price methodology.
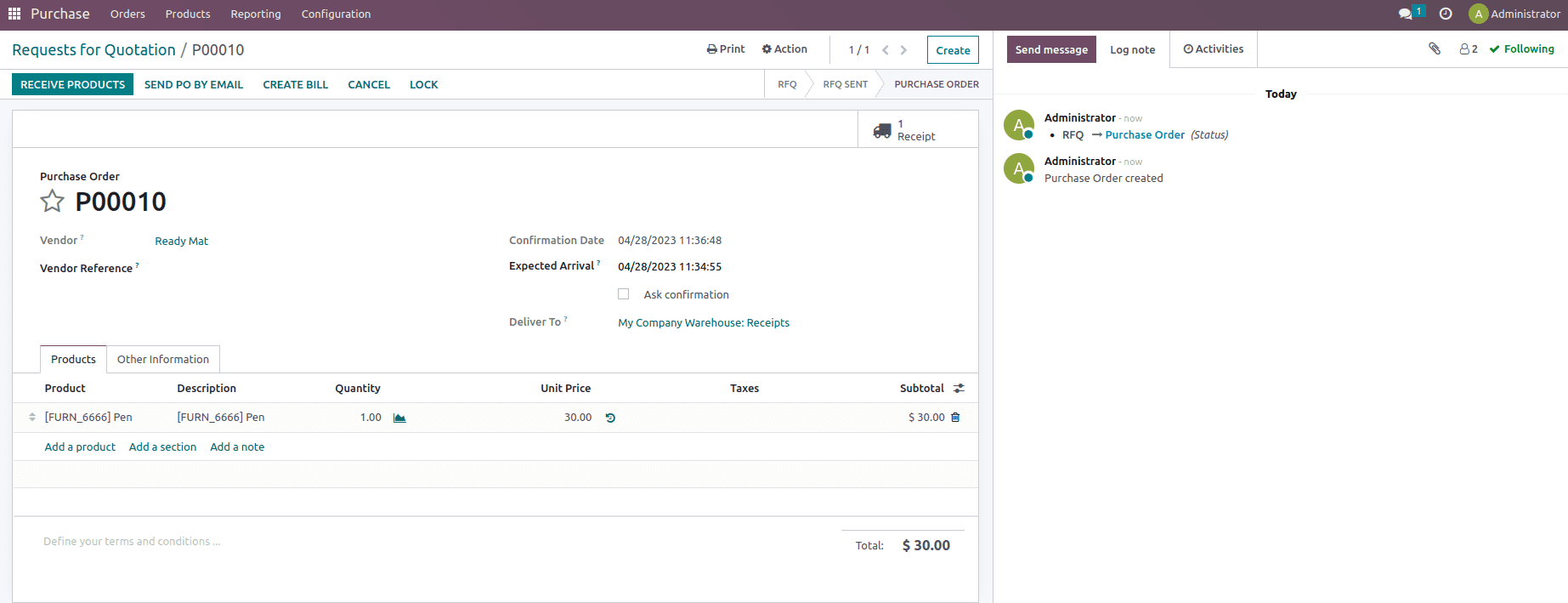
Here we have created a purchase order for the product Pen with the unit price mentioned as $30 and validate the receipt.
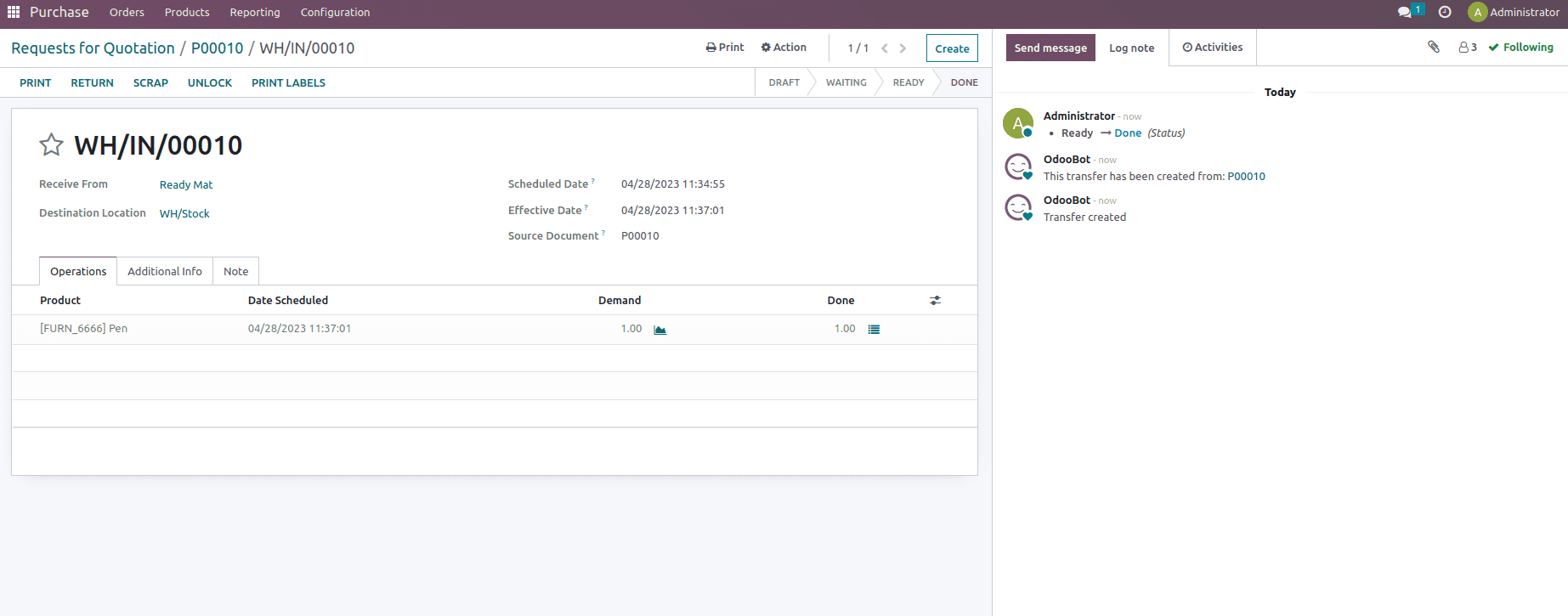
Once the purchase order is confirmed and validated, let’s check the inventory valuation generated for the product Pen.
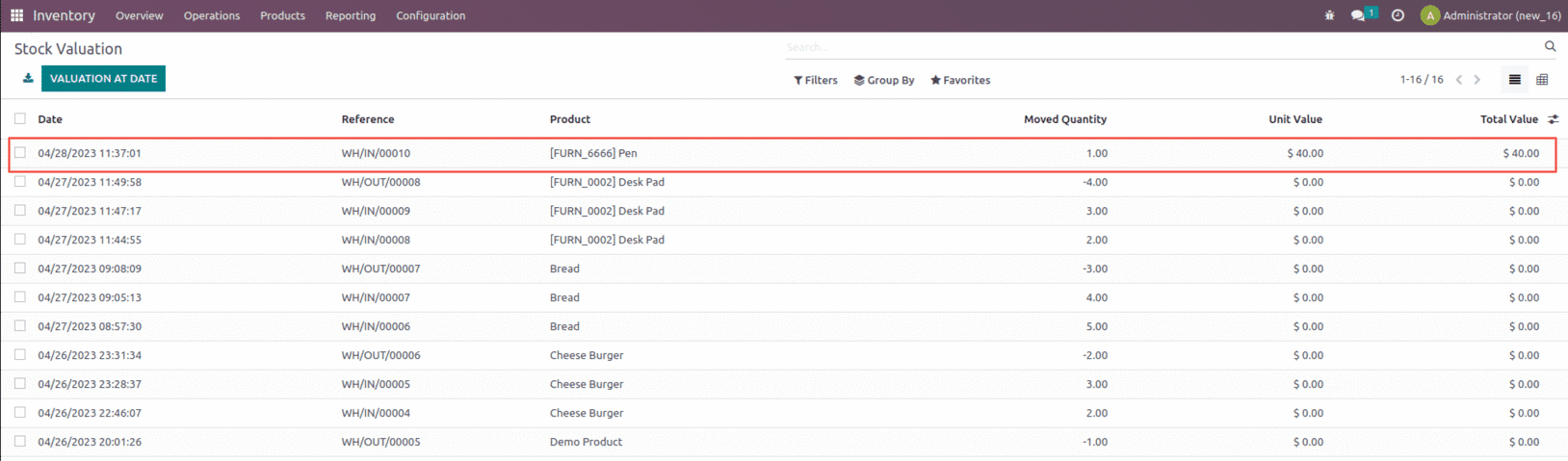
In a theoretical sense, we paid $30 for the product Pen, and when we check the Inventory Valuation report, we can see that for one quantity, the value added was $40 rather than the $30.
So for the Standard costing method, the standard price of the product is considered. The inventory valuation will not take into account the price you paid for this item. It takes the cost price you specified on the product master directly.
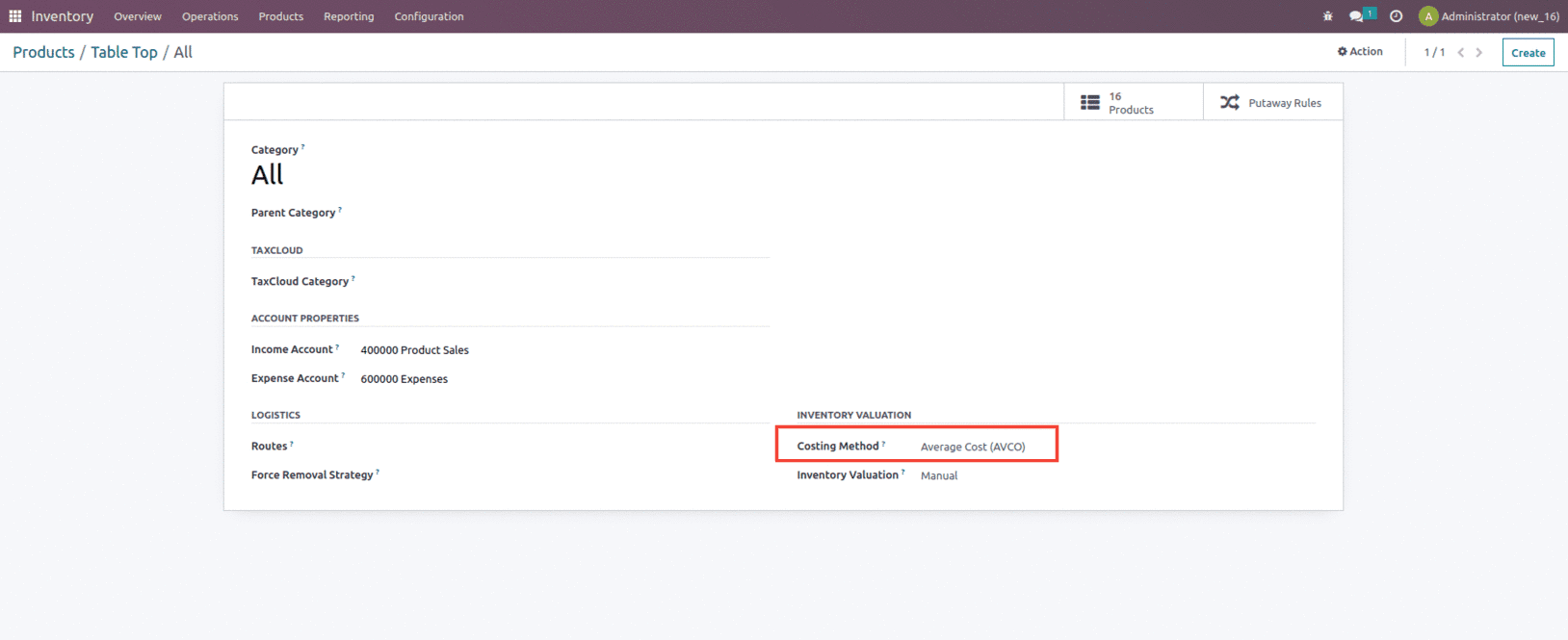
Average Costing Method
The average costing approach calculates the cost of inventory items based on the average cost of all available similar goods in inventory. This is the cost of an item in inventory divided by the number of items in stock.
Every time the product is purchased and received, the cost is updated depending on the purchase order paid and the quantity ordered. However, the cost is unaffected once the goods leave the warehouse.
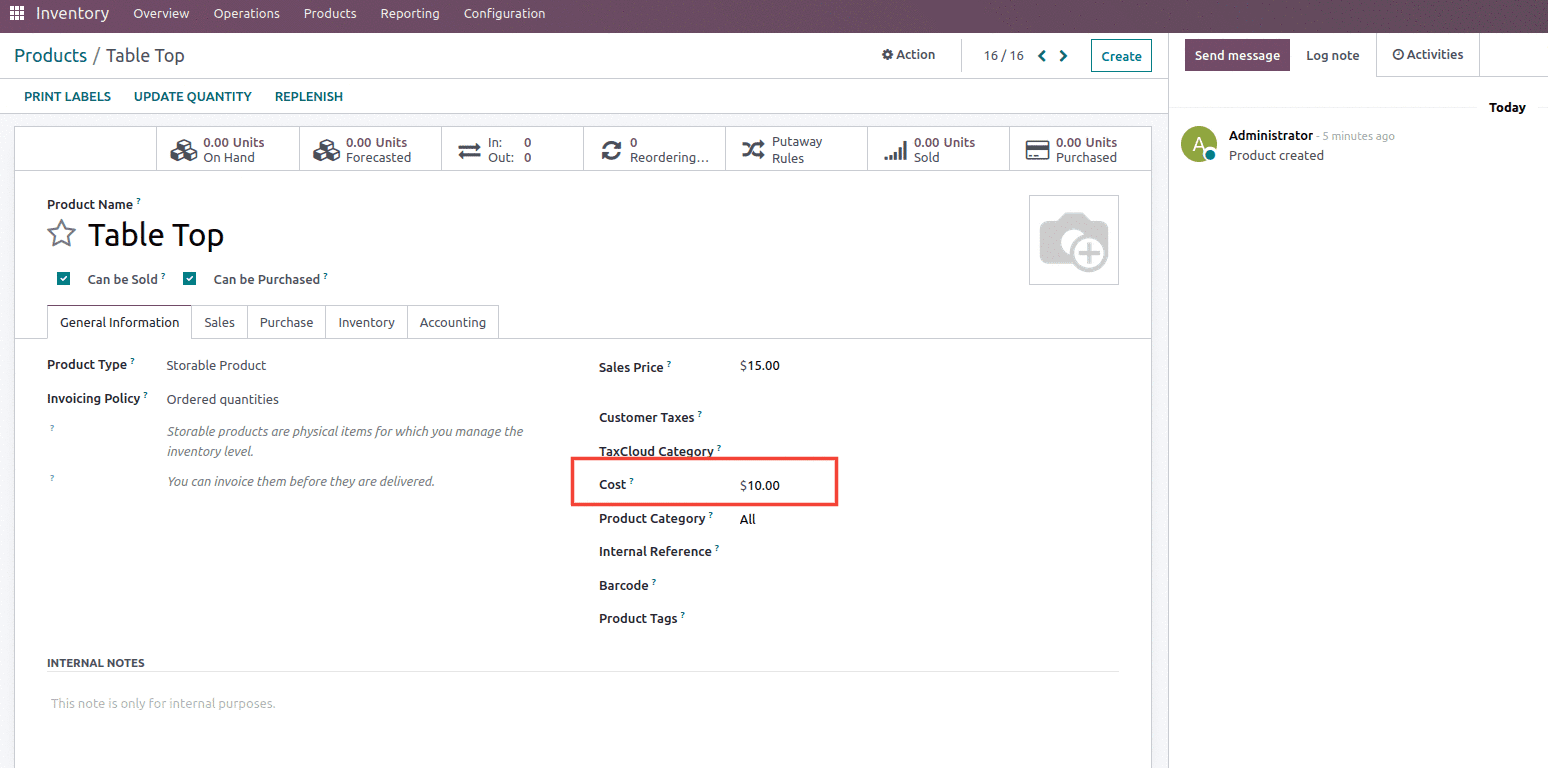
Let’s create a product with a cost set as $10 and a product category set as Average costing, as shown below.
Now to check the process, let us create the Purchase order for 10 quantities with unit price $10 and confirm the order.
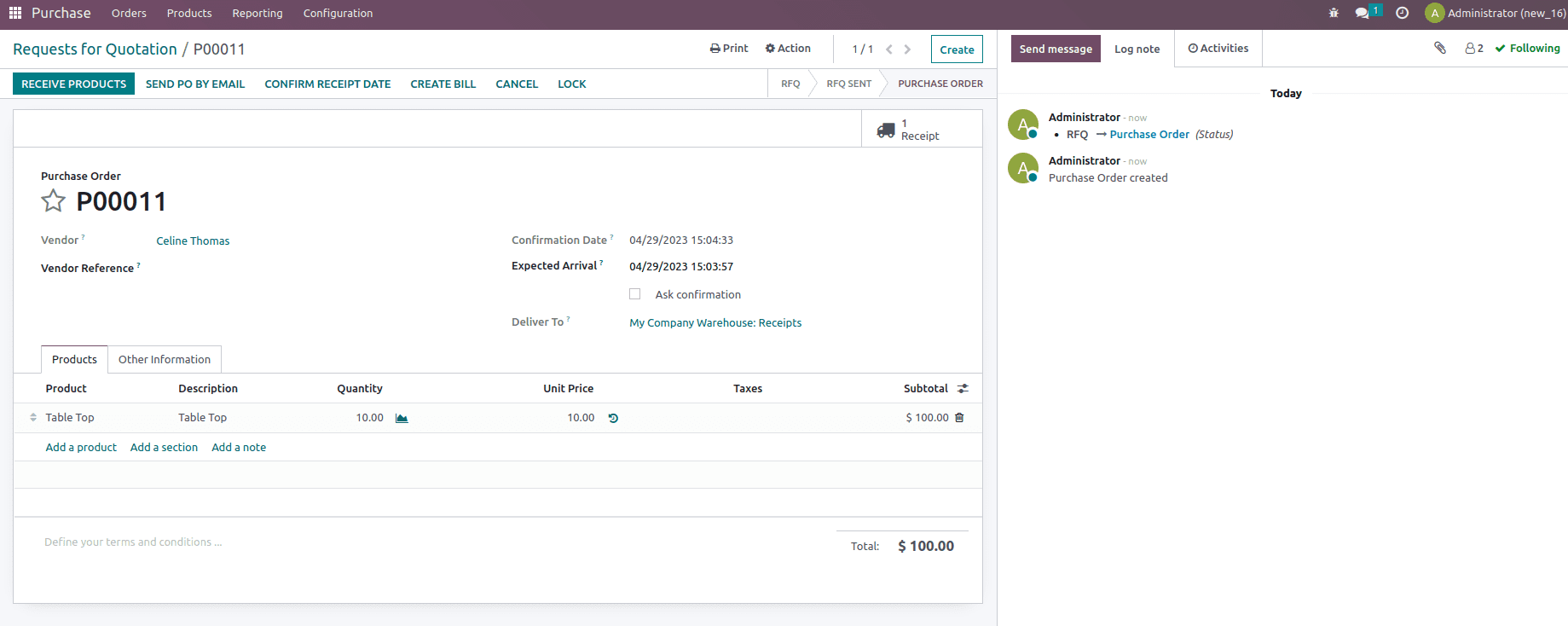
After validating the receipt, let’s check the inventory valuation created for the order from the inventory module.
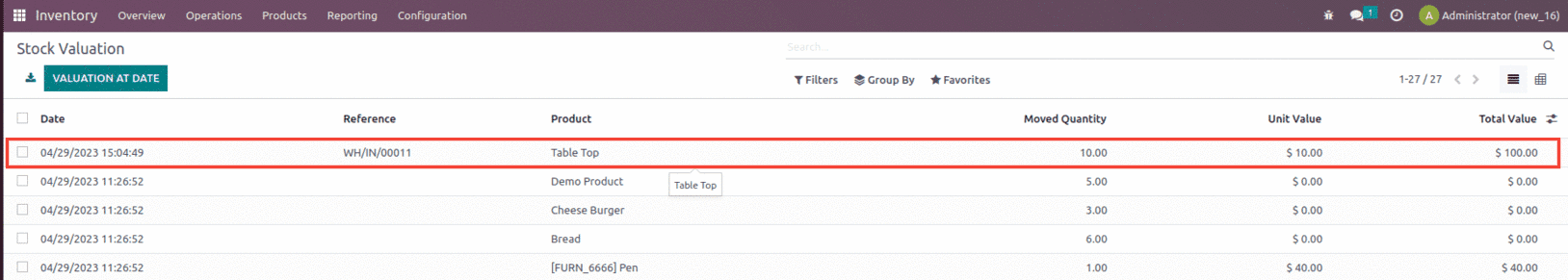
Again let’s create a Purchase order for the same product which includes 10 units for $150 and confirm the order as shown below.
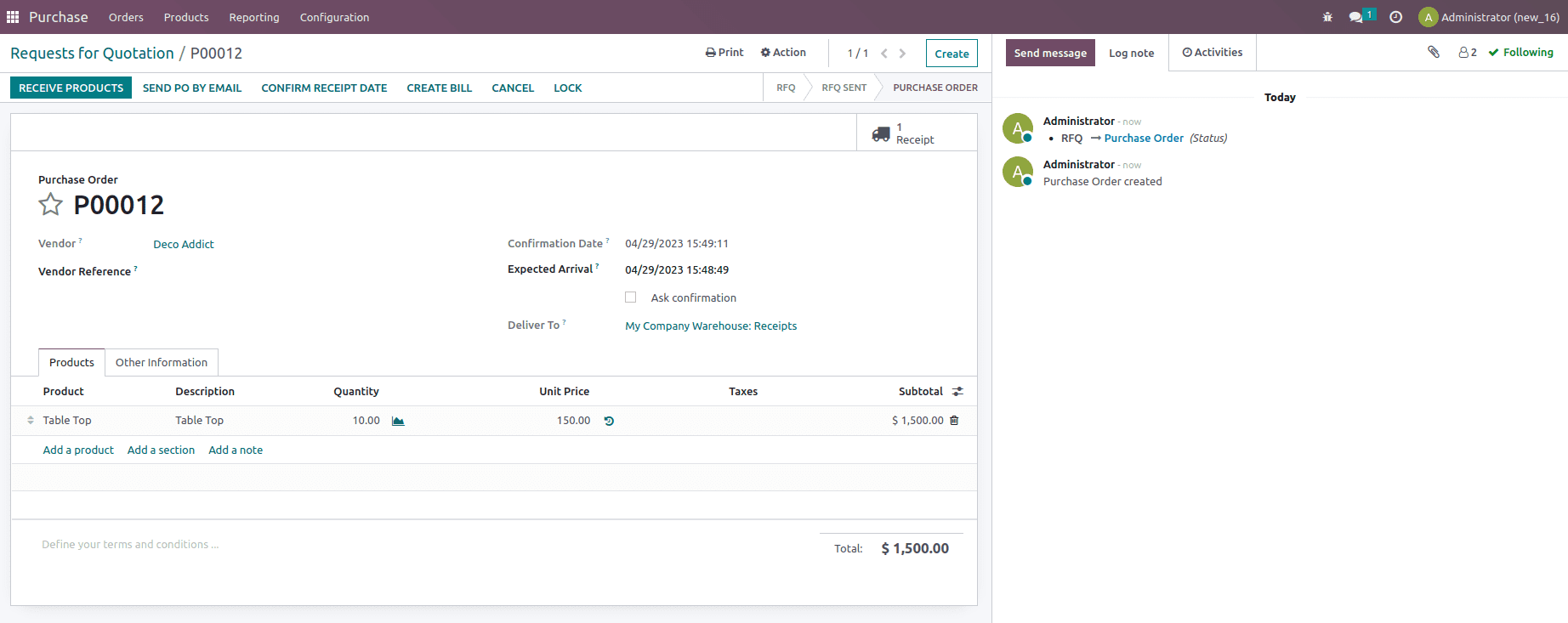
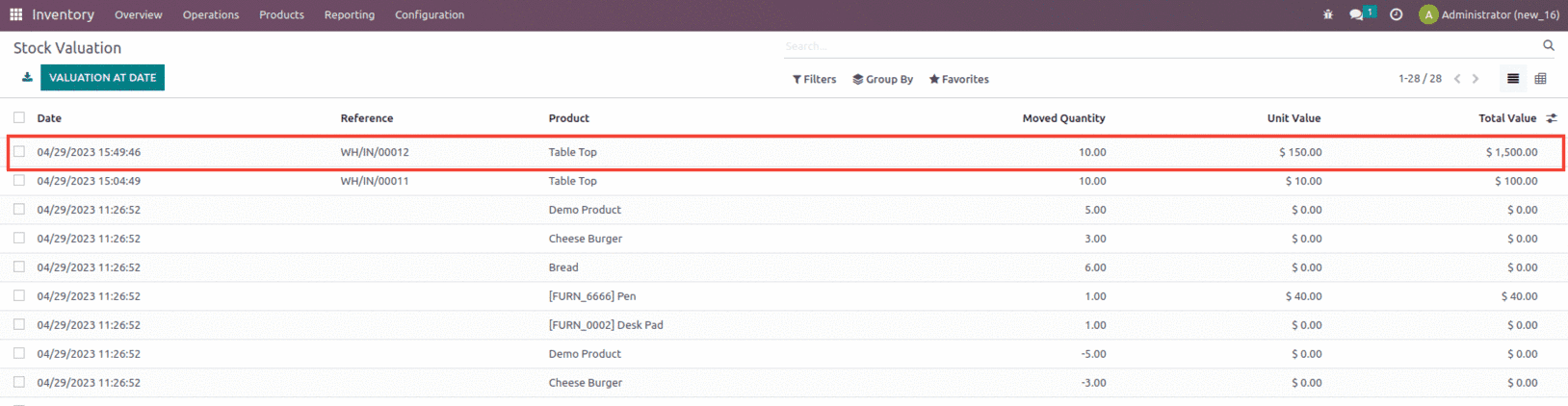
After validating the receipt, let’s check the inventory valuation created for the order from the inventory module.
Once the order is confirmed and validated and when we check the product, the product pricing is updated to $ 80, as shown below.
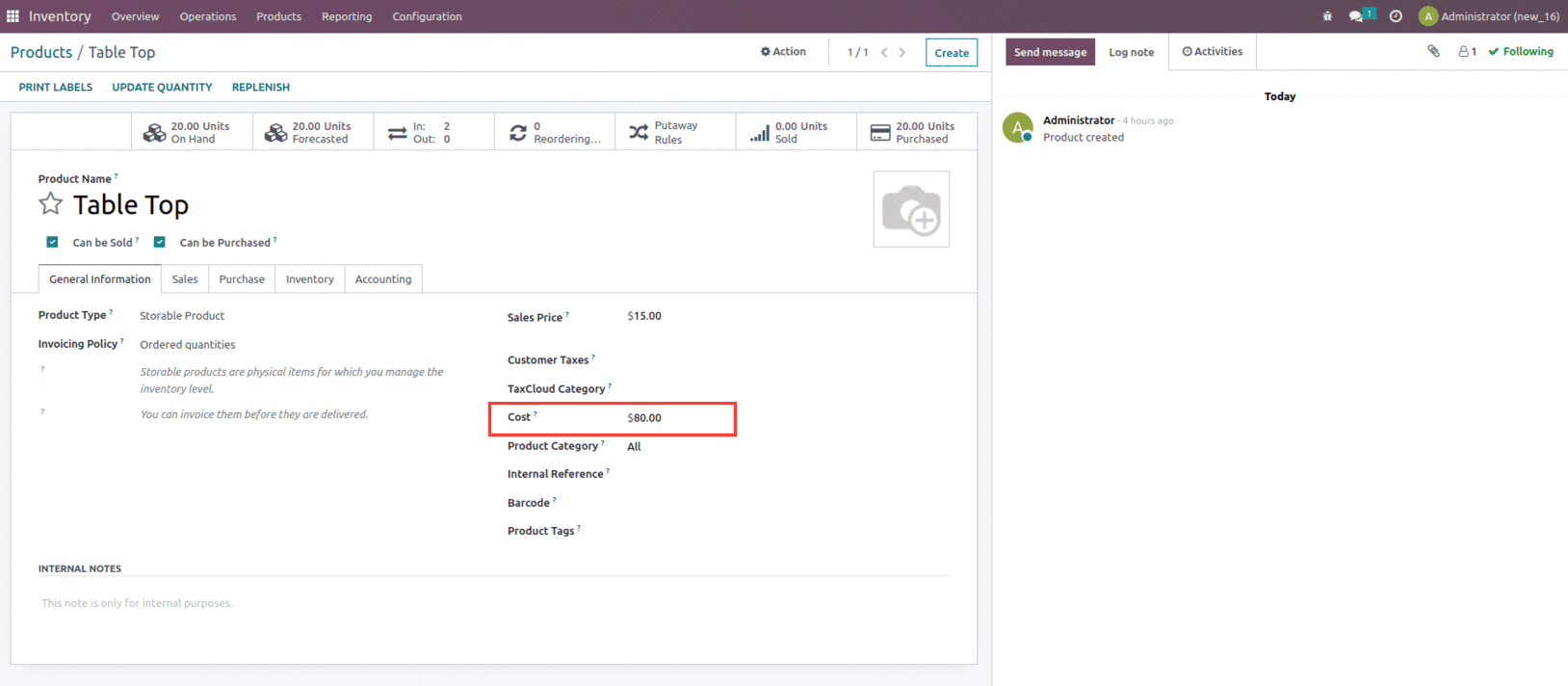
In the first purchase order, we purchased 10 units of a product with a $10 purchasing price. In that case, the Stock is worth $100, and the Unit Cost is $10. The second purchase order includes the same amount as the first, but the buying price has been raised to $150. As a result, the stock value for a second buy order is $1500. However, we consider the stock value for unit cost to be $1600, which is the sum of the stock values for the first and second purchase orders (1500+100). As a result, the unit cost for the second purchase order is $80 because the sum of stock value is $1600 and total quantity is 20.
First In First Out (FIFO)
This technique adjusts a product’s cost price based on the last existing product in the inventory. As a result, removal tactics such as FIFO have an impact on price.
To perform this operation, let us create a product with a costing method set as FIFO and Removal strategy also set as FIFO.
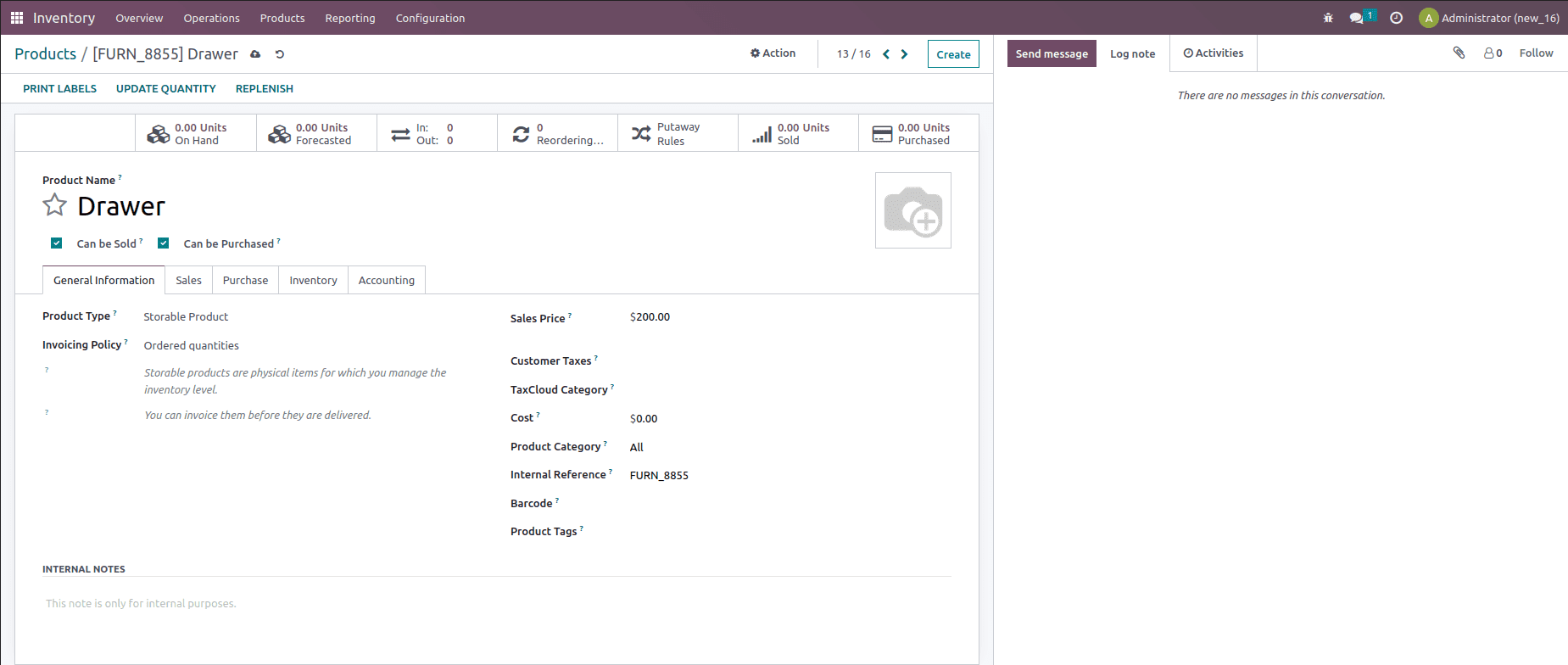
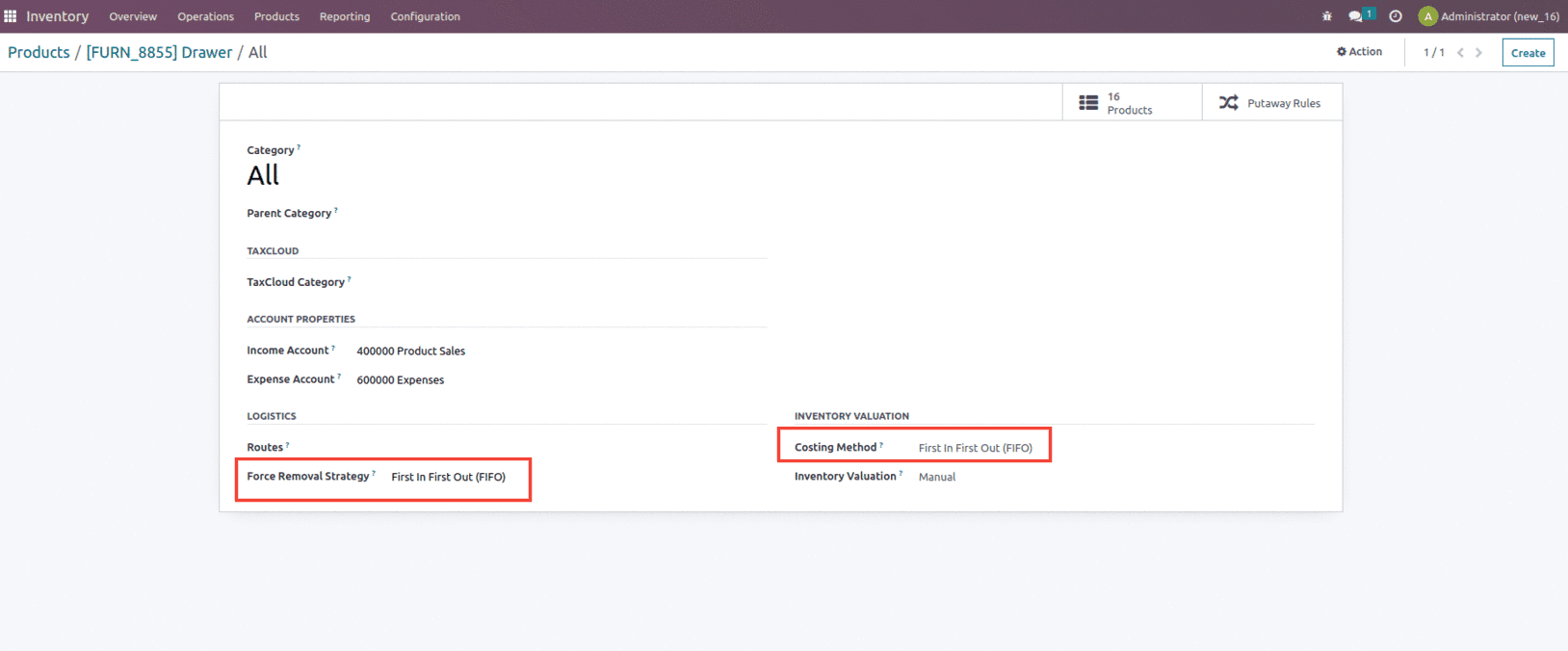
Now to check the working of this costing method, let us create a purchase order for two quantities of the product at a unit price $100.
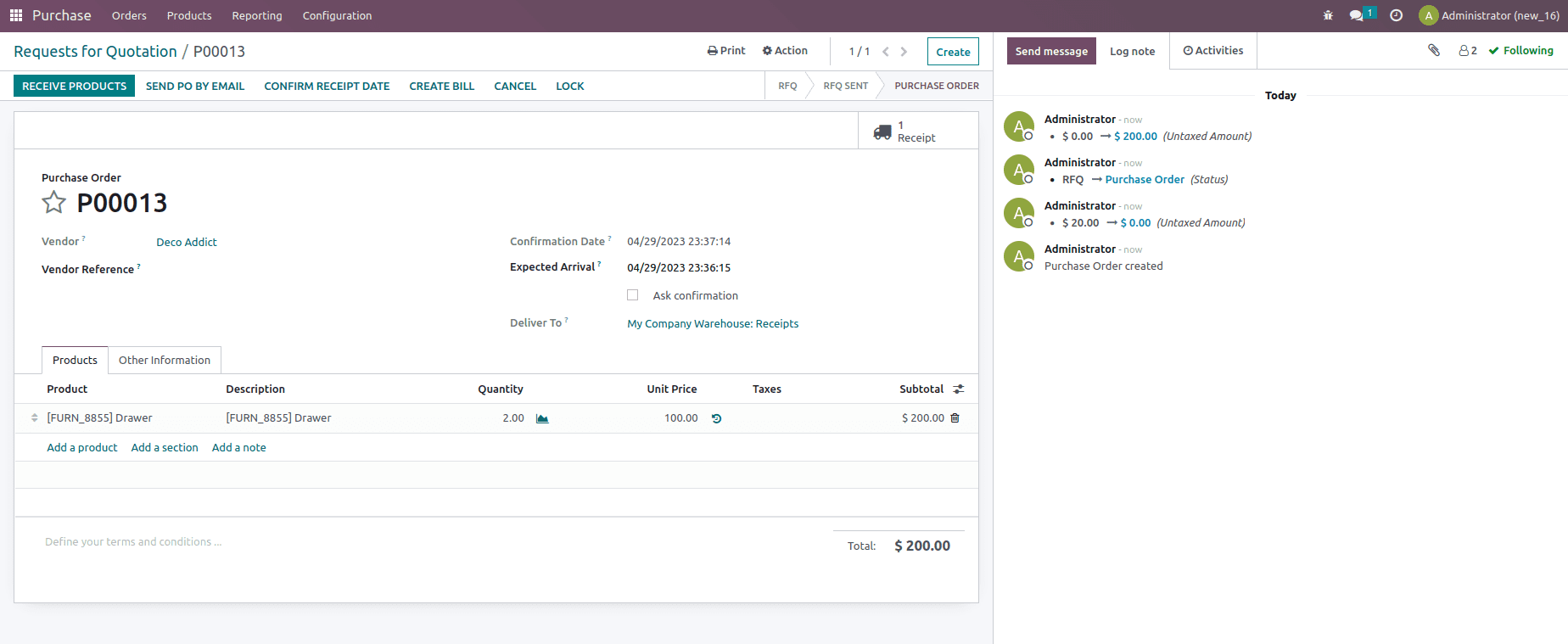
Confirm the purchase order and validate the reception once that is done. Now let’s create another purchaser order for two quantities of the product at unit price $150.
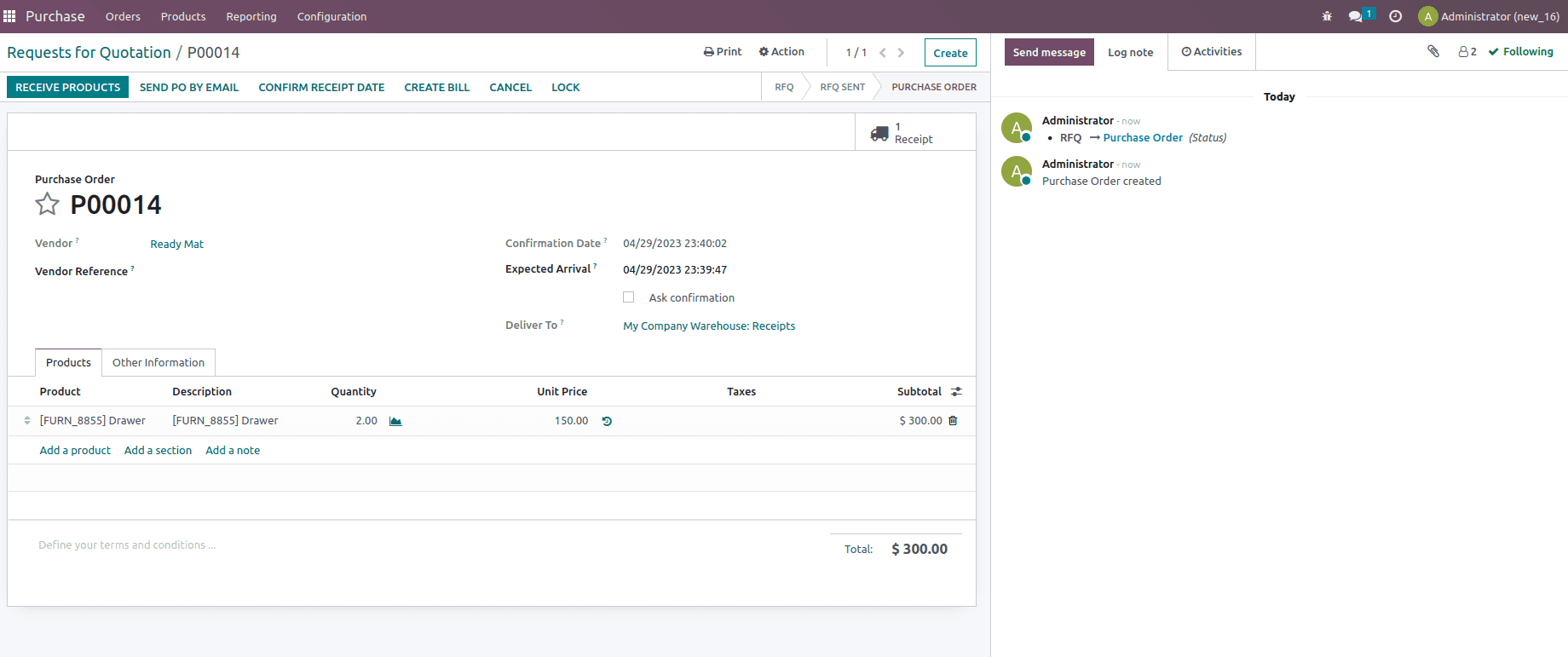
Confirm andvalidate the transfer. Once that is done, let us check the inventory valuationof the transfer that is created from the inventory module, as shown below.
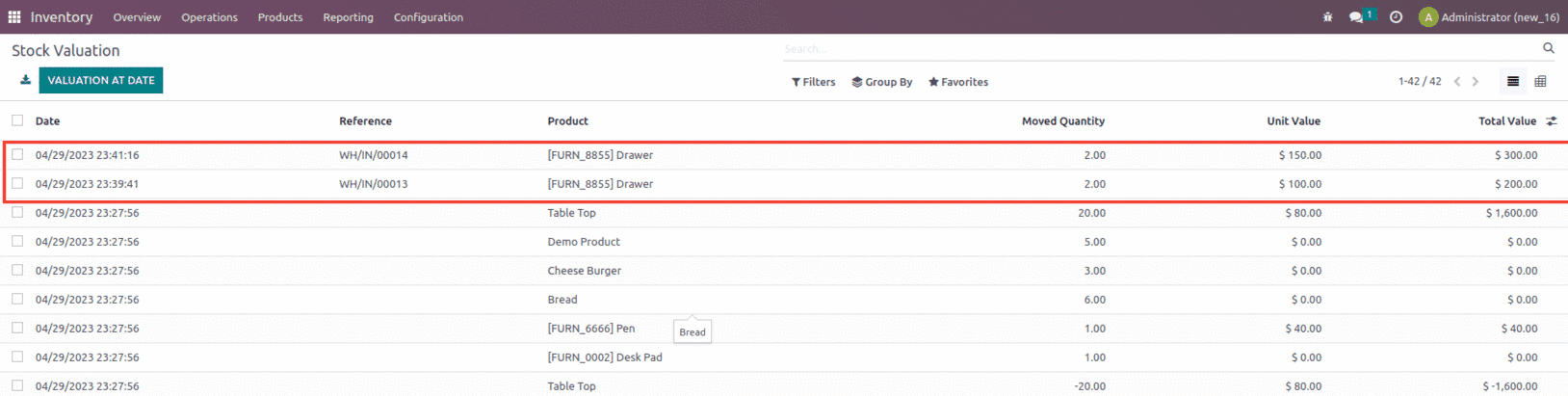
Now let us create a sale order and check how this costing method would work, create a sale order for two quantities with unit price set as $100 as shown below.
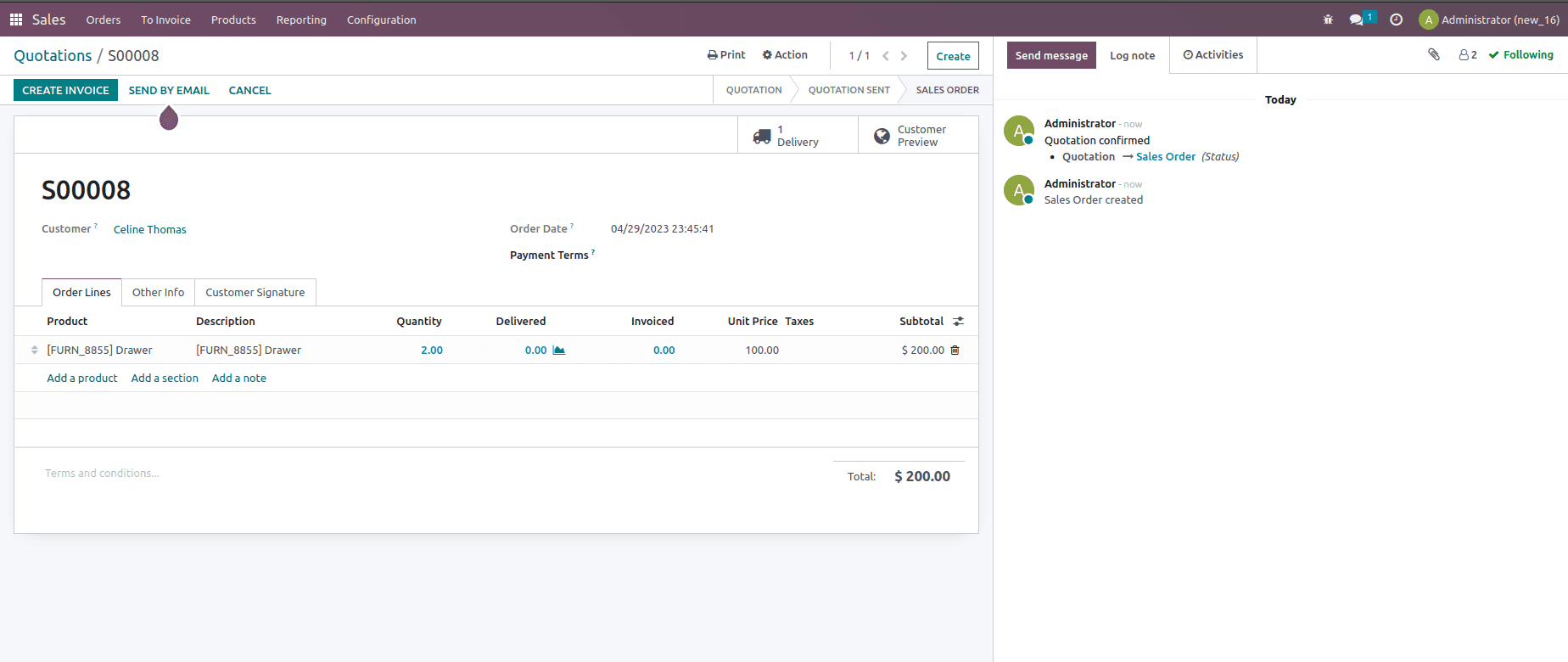
Confirm and validate the sale order. After validating the transfer, if we check the product, then the product cost will be updated to $150, as shown below.
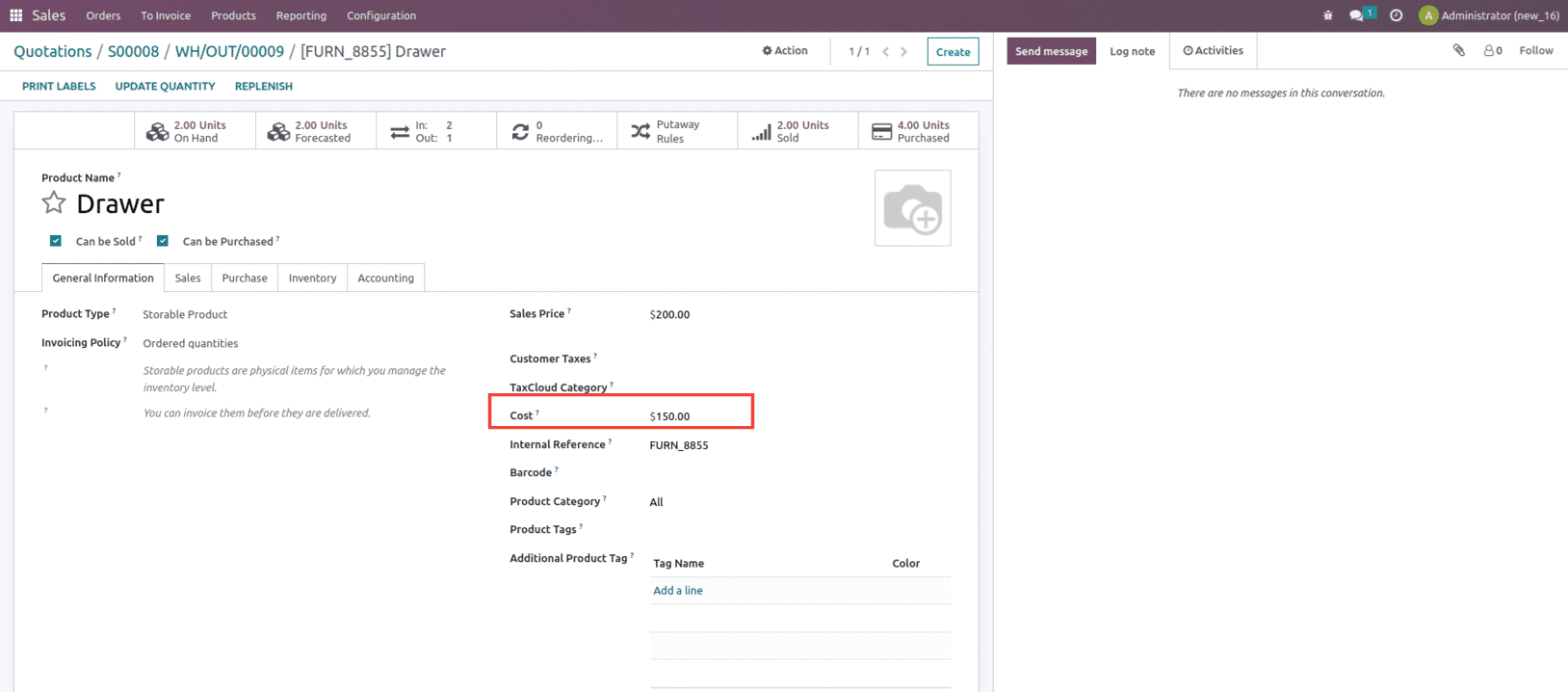
So we can say that the product’s cost price remains constant until it is removed from the inventory by one of the removal methods.
This is how the Costing method works in Odoo 16.


